Effects of surface treatments on the adhesion strengths between polyether ether ketone and both composite resins and poly(methyl methacrylate)
- PMID: 40483403
- PMCID: PMC12144709
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-025-06305-7
Effects of surface treatments on the adhesion strengths between polyether ether ketone and both composite resins and poly(methyl methacrylate)
Abstract
Background: This study evaluated the effects of three surface treatments-concentrated H2SO4, sodium borohydride (NaBH4), and their combination-on the shear bond strengths between polyether ether ketone (PEEK) and both composite resins and poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA).
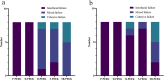
Methods: PEEK specimens (n = 160) were randomly assigned to composite resin and PMMA groups, each of which was subdivided into normal and aging groups (n = 40), each comprising samples that were pristine (untreated) or treated with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), NaBH4, or concentrated H2SO4 or sequentially treated with NaBH4 and concentrated H2SO4 (n = 8). The shear bond strength (SBS) of the normal and aged specimens were measured. For the normal and treated specimens, the surface and cross-sectional morphologies were analyzed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), the chemical bond modifications were investigated using X-ray photoelectron and attenuated total reflectance Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopies (XPS and ATR-FTIR, respectively), the mechanical strengths were measured using three-point bending tests, and the cytotoxicities were evaluated using cell-counting kit-8 (CCK-8) assays and 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) staining.
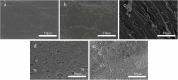
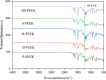
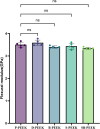
Results: NaBH4 etched the PEEK surface, generating a fibrous texture, while concentrated H2SO4 produced a surface possessing variously sized pores. Sequential treatment with NaBH4 and concentrated H2SO4 produced dense, permeating pores. XPS confirmed that NaBH4 reduced carbonyl groups to hydroxyl groups on the PEEK surface. ATR-FTIR spectroscopy confirmed that the silane coupling agent grafted onto the PEEK surface, forming Si-O-C bonds. NaBH4 and concentrated H2SO4 both strengthened the shear bonding between the PEEK and both the composite resins and PMMA (P < 0.05). The specimens sequentially treated with NaBH4 and 98% concentrated H2SO4 possessed the strongest shear bonding (P < 0.05). The aged specimens sequentially treated with NaBH4 and concentrated H2SO4 retained very strong shear bonds. CCK-8 cytotoxicity assays and DAPI staining confirmed that these surface treatments meet oral biocompatibility standards.
Conclusion: NaBH4 introduced chemical bonds to the PEEK surface, while concentrated-H2SO4-induced sulfonation enhanced the micromechanical interlocking between the PEEK and both the composite resins and PMMA. These combined physicochemical modifications significantly strengthened the adhesion between the PEEK and both the composite resins and PMMA and effectively strengthened PEEK's bonding.
Keywords: Composite resin; Poly(methyl methacrylate); Polyether ether ketone; SOdium Borohydride; Shear bond strength; Sulfonation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Surface modification of polyether ether ketone (PEEK) via sulfonation and hydroxyapatite coating: impact on shear bond strength with resin composite.Clin Oral Investig. 2025 Mar 15;29(4):184. doi: 10.1007/s00784-025-06256-x. Clin Oral Investig. 2025. PMID: 40088300
-
Effect of different surface treatments on PEEK-enamel bonds: Bonding durability and mechanism.J Prosthet Dent. 2025 Mar;133(3):892.e1-892.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2024.11.012. Epub 2024 Dec 20. J Prosthet Dent. 2025. PMID: 39709260
-
Effects of various laser applications on surface roughness and bond strength to veneering composites of polyether ether ketone (PEEK) and polyether ketone ketone (PEKK) materials.Lasers Med Sci. 2024 Nov 6;39(1):269. doi: 10.1007/s10103-024-04213-w. Lasers Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39500765
-
Surface Treatments and Adhesives Used to Increase the Bond Strength Between Polyetheretherketone and Resin-based Dental Materials: A Scoping Review.J Adhes Dent. 2022 May 16;24:233-245. doi: 10.3290/j.jad.b2288283. J Adhes Dent. 2022. PMID: 35575656 Free PMC article.
-
Overcoming biological inertness: multifaceted strategies to optimize PEEK bioactivity for interdisciplinary clinical applications.Biomater Sci. 2025 Jun 10;13(12):3106-3122. doi: 10.1039/d4bm01693a. Biomater Sci. 2025. PMID: 40314180 Review.
References
-
- Zol SM, Alauddin MS, Said Z, Mohd Ghazali MI, Hao-Ern L, Mohd Farid DA, Zahari NAH, Al-Khadim AHA, Abdul Aziz AH. Description of poly(aryl-ether-ketone) materials (PAEKs), polyetheretherketone (PEEK) and polyetherketoneketone (PEKK) for application as a dental material: a materials science review. Polymers (Basel). 2023;15(9):2170. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gama LT, Bezerra AP, Schimmel M, Rodrigues Garcia RCM, de Luca CG, Gonçalves T. Clinical performance of polymer frameworks in dental prostheses: a systematic review. J Prosthet Dent. 2024;131(4):579–90. - PubMed
-
- Valenti C, Federici MI, Coniglio M, Betti P, Pancrazi GP, Tulli O, Masciotti F, Nanussi A, Pagano S. Mechanical and biological properties of polymer materials for oral appliances produced with additive 3D printing and subtractive CAD-CAM techniques compared to conventional methods: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Oral Investig. 2024;28(7):396. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

