Comparative effectiveness of nitinol staple-only fixation versus antiglide plate fixation for Weber type B distal fibular fractures
- PMID: 40483452
- PMCID: PMC12144700
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-025-08835-1
Comparative effectiveness of nitinol staple-only fixation versus antiglide plate fixation for Weber type B distal fibular fractures
Abstract
Background: Interest in less invasive surgeries for Weber type B distal fibular fracture has increased recently. This study aimed to demonstrate that nitinol staple-only fixation is less invasive compared to antiglide plate fixation.
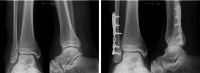
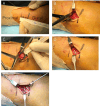
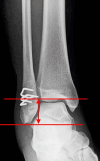
Materials and methods: This retrospective review involved 59 patients with Weber type B fibular fractures who underwent surgery between 2018 and 2023. Twenty-eight patients underwent antiglide plate fixation, whereas 31 underwent multiple nitinol staple-only fixation. The intraoperative assessment included skin incision length and operative time. The radiographic outcomes were bone union and fibular length. The clinical outcomes included delayed wound healing, infection, discomfort from the implant, implant removal, and the Self-Administered Foot Evaluation Questionnaire (SAFE-Q) score administered at the last visit.
Results: The mean skin incision length and operative time of nitinol staple-only fixation were 3.8 ± 0.5 cm and 19.6 ± 3.6 min, compared with 8.7 ± 1.3 cm and 48.8 ± 10.6 min for plate fixation, respectively. Bone union was confirmed in all patients without fibular shortening. Although no significant differences in patients with delayed wound healing, infection, or postoperative SAFE-Q scores were found between the two groups, more patients with plate fixation reported discomfort from the implant (71.4% vs. 32.3%) and requested its removal (75.0% vs. 35.5%).
Conclusion: Multiple nitinol staple-only fixations offer the advantages of a smaller skin incision, shorter operative time, lesser discomfort from the implants, and a reduced need for implant removal compared with antiglide plate fixation. Furthermore, staple-only fixation could achieve bone union without loss of correction. This suggests that multiple nitinol staple-only fixation may be less invasive and more beneficial for patients than antiglide plate fixation.
Keywords: Ankle fracture; Antiglide plates; Fibula fracture; Fracture fixation; Nitinol staples.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The responsible institutional review board of Shiseikai Daini Hospital approved this study (IRB number: 145). All participants approved the informed consent of the use of imaging and clinical data. This study was carried out in accordance with the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki. Consent for publication: Written informed consent to participate in this study and publish identifiable images or information was obtained from all participants, and parent/guardian consent was obtained for participants under the age of 18. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Hughes JL, Weber H, Willenegger HKE. Evaluation of ankle fractures: non-operative and operative treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979;138:11–9. - PubMed
-
- Giver Jensen T, Aqeel Khudhair Almadareb M, Booth Nielsen M, Jesper Hansen E, Lindberg-Larsen M. Outcome after treatment of distal fibula fractures using one-third tubular plate, locking compression plate or distal anatomical locking compression plate. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2023;62:524–8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

