Cholesterol metabolism regulated by CAMKK2-CREB signaling promotes castration-resistant prostate cancer
- PMID: 40483692
- PMCID: PMC12289408
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2025.115792
Cholesterol metabolism regulated by CAMKK2-CREB signaling promotes castration-resistant prostate cancer
Abstract
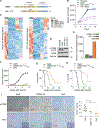
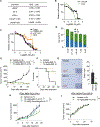
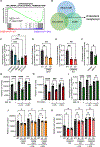
Castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) remains an incurable disease in need of improved treatments. CAMKK2 is an emerging therapeutic target whose oncogenic effects in prostate cancer have, to date, been largely attributed to its activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). Here, we demonstrate that CAMKK2 promotes prostate cancer growth through an alternative downstream pathway involving CAMKI and CREB. Unbiased transcriptomics identify CREB-mediated transcription as a CAMKK2-regulated process, findings that we validate using diverse molecular, genetic, and pharmacological approaches in vitro and in vivo. CAMKK2 promotes CREB phosphorylation/activation through CAMKIα independently of AMPK, CAMKIV, or other CAMKI isoforms. Functionally, the CREB family members CREB1 and ATF1 exhibit close redundancy, necessitating co-targeting for optimal anti-tumor efficacy. An inhibitor of CREB1/ATF1 blocks CRPC with minimal side effects. Mechanistically, CAMKK2 and CREB increase CRPC growth through augmenting cholesterol metabolism. Together, these findings identify an oncogenic pathway that could be exploited for the treatment of CRPC.
Keywords: AMPK; CAMKI; CAMKK2; CP: Cancer; CP: Metabolism; CREB; androgen receptor; cholesterol; metabolism; prostate cancer.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests D.E.F. has received research funding from GTx, Inc, and has a familial relationship with March Biosciences, Biocity Biopharmaceuticals, and Barricade Therapeutics. D.E.F. has also been issued a patent on CAMKK2 as a target in cancer (USP 9999620; EP 2606130).
Figures




References
-
- Frigo DE, Howe MK, Wittmann BM, Brunner AM, Cushman I, Wang Q, Brown M, Means AR, and McDonnell DP (2011). CaM kinase kinase beta-mediated activation of the growth regulatory kinase AMPK is required for androgen-dependent migration of prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res 71, 528–537. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-2581. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Karacosta LG, Foster BA, Azabdaftari G, Feliciano DM, and Edelman AM (2012). A regulatory feedback loop between Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2 (CaMKK2) and the androgen receptor in prostate cancer progression. J. Biol. Chem 287, 24832–24843. 10.1074/jbc.M112.370783. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sharma NL, Massie CE, Ramos-Montoya A, Zecchini V, Scott HE, Lamb AD, MacArthur S, Stark R, Warren AY, Mills IG, and Neal DE (2013). The androgen receptor induces a distinct transcriptional program in castration-resistant prostate cancer in man. Cancer Cell 23, 35–47. 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.11.010. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

