Interaction between the breast tumor microenvironment and gut microbiome
- PMID: 40484980
- PMCID: PMC12147490
- DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2025.2514136
Interaction between the breast tumor microenvironment and gut microbiome
Abstract
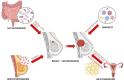
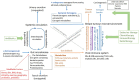
Previously believed to be sterile, the breast microenvironment has been revealed by modern DNA sequencing technologies to harbor a diverse community of microorganisms. The breast tumor microenvironment (TME) has a microbial signature unique to that of other breast pathologies as well as between breast cancer subtypes and stage. Among the plethora of microorganisms identified, Methylobacterium radiotolerans and Sphingomonas yanoikuyae stand out, both elevated in breast cancer tissue and associated with cancer stage. Breast cancer is the most common malignancy affecting women and the second most common cause of cancer-specific death in women worldwide. Gut dysbiosis has recently emerged as a key player, although the exact mechanisms are still unclear. Hypothesized mechanisms include bacterial metabolites inducing genomic instability, imbalances in the local and systemic immune system, the role of gut microbiota in the regulation of estrogen metabolism. Probiotic commensals Akkermansia muciniphila and Bifidobacterium appear to have a protective effect, with evidence of gut wall protection, correlation with less advanced disease and better treatment efficacy and tolerability. This review outlines the relationship between the breast microbiome, the gut microbiome, the 'estrabolome', and the immune system in breast cancer. This characterization could make a significant clinical contribution, potentially leading to new methods of primary prevention, better prognostication and prediction, as well as new avenues of treatment.
Keywords: Breast cancer; dysbiosis; estrabolome; microbiome; microbiota.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical