De novo variant in RING finger protein 213 causes systemic vasculopathy
- PMID: 40485582
- PMCID: PMC12220945
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.190094
De novo variant in RING finger protein 213 causes systemic vasculopathy
Abstract
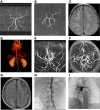
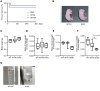
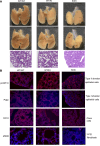
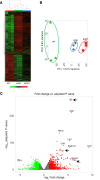
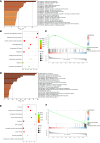
Systemic arterial stenosis, including moyamoya disease (MMD) and middle aortic syndrome (MAS), is a rare condition of unclear etiology. MMD is a cerebral angiopathy, and MAS affects the abdominal and thoracic aorta. Although some genetic associations with MAS have been identified, the causes remain elusive. In this study, de novo heterozygous missense variants of RING finger protein 213 (RNF213) (p.His4058Pro and p.Thr4155Pro) in 2 unrelated families with MAS and MMD were studied by whole-exome sequencing. To elucidate the significance of these variants, we produced knockin mice carrying the Rnf213 p.His4058Pro variant. Homozygous knockin mice exhibited perinatal lethality because of respiratory failure and lung dysplasia, suggesting that this variant is pathogenic. Lung dysplasia in homozygous knockin mice was associated with upregulated innate immunity and inflammatory responses and downregulated cell proliferation. These findings suggested that in mice, the RNF213 p.His4058Pro variant plays critical roles in regulation of innate immunity and inflammation that affect lung development, revealing the complexity of RNF213 function in various tissues and species. In conclusion, this study provides insights into the genetic basis of MAS and MMD, highlights the potential involvement of RNF213 variants in systemic vasculopathy, and identifies unexpected associations with lung development and immune processes.
Keywords: Development; Genetic diseases; Innate immunity; Vascular biology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

