Mechanistic Foundations of KRAS-Driven Tumor Ecosystems: Integrating Crosstalk among Immune, Metabolic, Microbial, and Stromal Microenvironment
- PMID: 40485603
- PMCID: PMC12376694
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202502714
Mechanistic Foundations of KRAS-Driven Tumor Ecosystems: Integrating Crosstalk among Immune, Metabolic, Microbial, and Stromal Microenvironment
Abstract
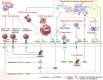
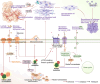
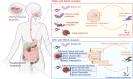
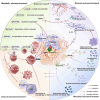
Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog (KRAS) is the most frequently mutated member of the RAS family of small GTPases (RAS). It affects about one-fifth of cancer cases. The tumor microenvironment (TME) is a multifaceted network of immune cells, metabolites, microbiota, stromal components, and extracellular matrix. It creates a dynamic ecosystem that supports malignant initiation, progression, and therapy resistance through bidirectional crosstalk with tumor cells. Emerging evidence reveals distinct TME landscapes shaped by wild-type versus oncogenic KRAS variants. Additionally, TME rewiring occurs during KRAS-targeted therapies. Deciphering these KRAS-dependent TME architectures and their therapeutic vulnerabilities represents a critical frontier for precision oncology. This review synthesizes key milestones and persistent challenges in KRAS inhibitor development. And it systematically evaluates how KRAS mutations orchestrated immunosuppressive niches, metabolic symbiosis, stromal remodeling, and microbiome dysbiosis, supported by mechanistic insights from preclinical and clinical studies. It further explores therapeutic opportunities arising from targeting TME interactions, including rational combinations of KRAS inhibitors with immune checkpoint blockade, metabolic agents, or microbiota-modulating strategies.
Keywords: KRAS; cancer; immunity; metabolism; microbiota; microenvironment; stroma.
© 2025 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- a) Scharpf R. B., Balan A., Ricciuti B., Fiksel J., Cherry C., Wang C., Lenoue‐Newton M. L., Rizvi H. A., White J. R., Baras A. S., Anaya J., Landon B. V., Majcherska‐Agrawal M., Ghanem P., Lee J., Raskin L., Park A. S., Tu H., Hsu H., Arbour K. C., Awad M. M., Riely G. J., Lovly C. M., Anagnostou V., Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 4058; - PMC - PubMed
- b) Lee J. K., Sivakumar S., Schrock A. B., Madison R., Fabrizio D., Gjoerup O., Ross J. S., Frampton G. M., Napalkov P., Montesion M., Schutzman J. L., Ye X., Hegde P. S., Nagasaka M., Oxnard G. R., Sokol E. S., Ou S. I., Shi Z., NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2022, 6, 91. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boriack‐Sjodin P. A., Margarit S. M., Bar‐Sagi D., Kuriyan J., Nature 1998, 394, 337. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82173342/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82203015/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82373275/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82403920/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2024JJ6662/Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province
- 2025JJ20077/Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province
- 2024RC3042/Science and Technology Innovation Program of Hunan Province
- 2023Q01/Youth Science Foundation of Xiangya Hospital
- GZC20242044/Postdoctoral Fellowship Program of the CPSF
- 2024M753679/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
- kq2403008/Nature Science Foundation of Changsha
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
