Clinical prognosis evaluation of alpha-fetoprotein-positive gastric cancer: comprehensive analysis and development of a novel nomogram for survival prediction
- PMID: 40485723
- PMCID: PMC12141012
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1598337
Clinical prognosis evaluation of alpha-fetoprotein-positive gastric cancer: comprehensive analysis and development of a novel nomogram for survival prediction
Abstract
Background: Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is an established biomarker for liver cancer, but its role in gastric cancer (GC) remains unclear. This study evaluated AFP's prognostic value in GC and developed a survival prediction model incorporating AFP and other clinical factors.
Methods: We analyzed 766 GC patients from Changzhou Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, categorizing them as AFP-positive (>20 ng/mL) or AFP-negative (≤20 ng/mL). Kaplan-Meier and Cox regression analyses assessed the association between AFP levels and overall survival (OS). A nomogram based on identified prognostic factors was created and evaluated using ROC curves, calibration curves, and decision curve analysis (DCA).
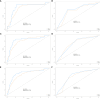
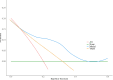
Results: Among 766 gastric cancer (GC) patients, 3.3% (n=25) exhibited elevated AFP levels (>20 ng/mL). The AFP-positive group demonstrated significantly more aggressive clinicopathological features, including larger tumor size (p < 0.05), deeper invasion (higher T-stage), increased lymph node metastasis (higher N-stage), and higher rates of distant metastasis (p = 0.035). Survival analysis revealed markedly worse outcomes for AFP-positive patients (Log-rank P < 0.001), with a 68% higher mortality risk (unadjusted HR =1.68, 95% CI: 1.27-2.23). Multivariate Cox regression confirmed AFP positivity as an independent prognostic factor (adjusted HR = 1.8, 95% CI: 1.03-3.14, p =0.04), alongside T4-stage, N3-stage, and distant metastasis. A prognostic nomogram integrating AFP levels and TNM staging achieved superior predictive accuracy (AUCs: 0.80-0.84) compared to TNM staging alone (AUCs: 0.70-0.74) across 1-, 3-, and 5-year survival. Calibration and decision curve analyses further validated the model's clinical utility, supporting its role in risk stratification and treatment planning.
Conclusions: AFP is a significant independent prognostic factor in gastric cancer, and its inclusion in a multivariate model enhances survival prediction. The prognostic nomogram developed in this study offers clinicians a valuable tool for predicting patient outcomes and guiding treatment decisions. Further validation and prospective studies are necessary to confirm the model's clinical applicability.
Keywords: alpha-fetoprotein; gastric cancer; metastasis; nomogram; prognosis.
Copyright © 2025 Zuo, Tan, Mao, Tang and Luo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Risk factors and nomogram construction for predicting long-term survival in hepatoid adenocarcinoma of the stomach].Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2025 Feb 25;28(2):157-168. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn441530-20240910-00312. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 39971567 Chinese.
-
Survival prognostic nomogram for young metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: a study of the US SEER database and a Chinese cohort.Front Oncol. 2025 Feb 14;15:1502253. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1502253. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40027127 Free PMC article.
-
A nomogram model based on the number of examined lymph nodes-related signature to predict prognosis and guide clinical therapy in gastric cancer.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 2;13:947802. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.947802. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36405735 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of survival and analysis of prognostic factors for patients with AFP negative hepatocellular carcinoma: a population-based study.BMC Gastroenterol. 2024 Mar 4;24(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s12876-024-03185-z. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38438972 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha fetoprotein (AFP)-producing gastric cancer: clinicopathological features and treatment strategies.Cell Biosci. 2025 Jun 10;15(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s13578-025-01424-8. Cell Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40495217 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

