Hotspots and frontiers of the relationship between gastric cancer and cancer-associated fibroblasts: a bibliometric analysis
- PMID: 40485724
- PMCID: PMC12140985
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1576696
Hotspots and frontiers of the relationship between gastric cancer and cancer-associated fibroblasts: a bibliometric analysis
Abstract
Background: Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts (CAFs) are pivotal stromal constituents within the Tumor Microenvironment (TME), characterized by marked heterogeneity and plasticity. Over the past two decades, a notable association between Gastric Cancer (GC) and CAFs has been established. Despite this, there remains a paucity of comprehensive data to guide researchers in understanding the prevalence and potential research trajectories concerning GC and CAFs.
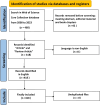
Methods: This study conducted an extensive literature search within the Web of Science Core Collection database from January 1, 2003, to December 31, 2023. Bibliometric analysis and visualization were performed using VOSviewer, CiteSpace, R software, and Microsoft Excel.
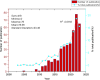
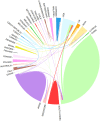
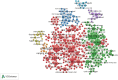
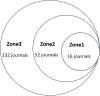
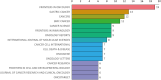
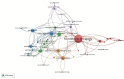
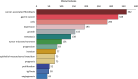
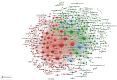
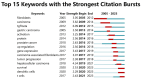
Results: A total of 1170 articles were included. These articles were disseminated across 200 journals and incorporated 1800 distinct keywords. A notable surge in publications has been observed from 2011 to 2023. China emerged as the leading contributor to both article count and citations. Prominent research institutions in this domain include Osaka City University, Shanghai Jiaotong University, and National Cancer Research Center Hospital. Notable researchers, such as Masakazu Yashiro and Kosei Hirakawa from Osaka City University and Zhenggang Zhu from Shanghai Jiaotong University, were among the most productive and highly cited authors. FRONTIERS IN ONCOLOGY boasts the highest number of publications, whereas ONCOGENE ranks as the most cited journal. The primary research foci within the realm of CAFs and GC encompass the impact of CAFs on GC cell proliferation, angiogenesis, invasion, metastasis, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, immunosuppression, drug resistance, and the interplay between CAFs and GC.
Conclusion: Using bibliometric analysis, this study presents a panoramic view of the research landscape of CAFs and GC from 2003 to 2023. It highlights prominent research areas and anticipates future directions with the aim of offering valuable insights and strategic recommendations for future endeavors in this field.
Keywords: bibliometrics; cancer-associated fibroblasts; gastric cancer; hot spot; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2025 Hu, Ren, Zhu, Shen, Qian, Chen and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A bibliometric and visual analysis of cancer-associated fibroblasts.Front Immunol. 2023 Dec 19;14:1323115. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1323115. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38173726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current perspectives and trends of CD39-CD73-eAdo/A2aR research in tumor microenvironment: a bibliometric analysis.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 12;15:1427380. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1427380. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39188712 Free PMC article.
-
Research hotspots and frontiers of machine learning in renal medicine: a bibliometric and visual analysis from 2013 to 2024.Int Urol Nephrol. 2025 Mar;57(3):907-928. doi: 10.1007/s11255-024-04259-3. Epub 2024 Oct 30. Int Urol Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39472403 Review.
-
Mapping knowledge structure and themes trends of cancer-associated fibroblasts: a text-mining study.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Dec 4;10:1302016. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1302016. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 38111465 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between gut microbiota and tumor immune microenvironment: A bibliometric and visualized study.World J Clin Oncol. 2025 Feb 24;16(2):101611. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i2.101611. World J Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39995564 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

