A Comparative Outcome of Full Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy for L4/5 Central-Paracentral Disc Herniation: Interlaminar versus Transforaminal Approach: A 2-Year Prospective Randomized Controlled Follow-Up Study
- PMID: 40485788
- PMCID: PMC12136931
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0044-1801376
A Comparative Outcome of Full Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy for L4/5 Central-Paracentral Disc Herniation: Interlaminar versus Transforaminal Approach: A 2-Year Prospective Randomized Controlled Follow-Up Study
Abstract
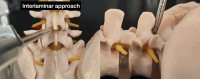
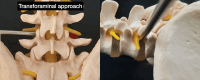
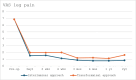
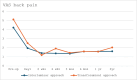
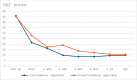
Background The interlaminar and transforaminal approaches are commonly employed in full endoscopic lumbar spine surgery. Both approaches are well-suited for addressing specific types of lumbar disc herniation, particularly at the L4/5 level. Objective This article compares the clinical outcomes of full endoscopic discectomy for L4/5 central-paracentral disc herniation between the interlaminar and transforaminal approaches. Materials and Methods Sixty patients were randomly assigned to either a full endoscopic interlaminar discectomy group or a full endoscopic transforaminal discectomy group, with 30 patients each. The procedures were performed by a single spine surgeon at our institution between 2017 and 2019. Over a 2-year follow-up period, various parameters, including operative time, postoperative hospitalization duration, Visual Analog Scale (VAS) scores for leg and back pain, Oswestry Disability Index (ODI), and modified MacNab criteria, were assessed and compared between the two groups. Additionally, the complication rates were documented. Results The two full endoscopic approaches resulted in significant improvements in back-leg pain measured by the VAS and in the ODI scores postsurgery. A comparison between the two approaches revealed a significant difference in the ODI score at the 6-week postoperative mark ( p = 0.02). However, other clinical outcome parameters did not show significant differences at the other follow-up time points. Postoperative dysesthesia was more prevalent in patients who underwent endoscopic transforaminal discectomy ( p < 0.05). The operative time was notably longer for the interlaminar approach compared with the transforaminal approach (62.6 ± 18.0 vs. 37.0 ± 13.6). Postoperative hospitalization time did not exhibit significant differences between the two groups. Conclusion Both the interlaminar and transforaminal approaches demonstrate similar clinical outcomes in treating central-paracentral L4/5 disc herniation. Each technique presents distinct advantages and disadvantages regarding operative time and postoperative dysesthesia. The full endoscopic interlaminar and transforaminal approaches have proven to be safe and effective methods for addressing L4/5 central-paracentral disc herniation.
Keywords: discectomy; full endoscope; interlaminar approach; lumbar disc herniation; transforaminal approach.
Asian Congress of Neurological Surgeons. This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonDerivative-NonCommercial License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit. Contents may not be used for commercial purposes, or adapted, remixed, transformed or built upon. ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transforaminal Percutaneous Endoscopic Discectomy for L3/4 and L4/5 Foraminal and Extraforaminal Lumbar Disc Herniation: Clinical Outcomes and Technical Note.Asian J Neurosurg. 2025 Mar 10;20(2):337-343. doi: 10.1055/s-0045-1805018. eCollection 2025 Jun. Asian J Neurosurg. 2025. PMID: 40485789 Free PMC article.
-
Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy via Transforaminal Approach Combined with Interlaminar Approach for L4/5 and L5/S1 Two-Level Disc Herniation.Orthop Surg. 2021 May;13(3):979-988. doi: 10.1111/os.12862. Epub 2021 Apr 5. Orthop Surg. 2021. PMID: 33821557 Free PMC article.
-
Minimally invasive discectomy versus microdiscectomy/open discectomy for symptomatic lumbar disc herniation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Sep 4;2014(9):CD010328. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010328.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 25184502 Free PMC article.
-
Endoscopic discectomy for L4-L5 disc herniation: percutaneous endoscopic transforaminal discectomy vs. unilateral biportal endoscopic discectomy.Front Surg. 2025 Jun 20;12:1565165. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2025.1565165. eCollection 2025. Front Surg. 2025. PMID: 40620698 Free PMC article.
-
Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy for L5S1 Lumbar Disc Herniation Using a Transforaminal Approach Versus an Interlaminar Approach: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.World Neurosurg. 2018 Aug;116:412-420.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2018.05.075. Epub 2018 May 18. World Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 29783008
References
-
- Phan K, Xu J, Schultz K et al. Full-endoscopic versus micro-endoscopic and open discectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of outcomes and complications. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2017;154:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Pruttikul P, Chobchai W, Pluemvitayaporn T, Kunakornsawat S, Piyaskulkaew C, Kittithamvongs P. Comparison of post-operative wound pain between interlaminar and transforaminal endoscopic spine surgery: which is superior? Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2022;32(05):909–914. - PubMed
-
- Ruetten S, Komp M, Merk H, Godolias G. Full-endoscopic interlaminar and transforaminal lumbar discectomy versus conventional microsurgical technique: a prospective, randomized, controlled study. Spine. 2008;33(09):931–939. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

