Outcomes and predictive factors after second stereotactic radiosurgery for refractory trigeminal neuralgia
- PMID: 40485909
- PMCID: PMC12141082
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ctro.2025.100969
Outcomes and predictive factors after second stereotactic radiosurgery for refractory trigeminal neuralgia
Abstract
ObjectivesThis study evaluates the safety and efficacy of Gamma Knife Stereotactic Radiosurgery (GKSRS) retreatment (T2) for recurrent or refractory trigeminal neuralgia (TN) following an initial SRS treatment (T1).
Methods: We analyzed 53 patients who underwent T2 between 2012 and 2018 using a prospectively maintained single institution database. Baseline characteristics, treatment details, and toxicity data were assessed, with pain responses evaluated via Barrow Neurological Institute (BNI) pain intensity scores. Predictors of pain recurrence and chronic sensory toxicity were identified using univariate and multivariable analyses.
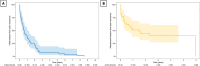
Results: The median T2 maximum dose was 70 Gy, primarily targeting the cisternal segment (43 %) and retrogasserian zone (RGZ) (34 %). Following T2, 95 % experienced initial pain relief with a 1-month median time to response, and 1-, 2-, and 3-year freedom from pain recurrence of 51 %, 45 %, and 41 %, respectively. Chronic sensory deficits were observed in 62 % of patients, but motor toxicity remained rare (mastication deficit: 2.5 %; facial motor deficit: 5.1 %). RGZ targeting (HR = 3.84, p = 0.02) and single isocenter treatments (HR = 3.85, p = 0.04) were predictive of pain recurrence when compared to dorsal root entry zone (DREZ) targeting and two isocenters, respectively. Affected trigeminal nerve length <11.5 mm was associated with chronic sensory deficits (OR = 7.14, p = 0.02).
Conclusion: GKSRS provides effective pain relief and manageable toxicity in retreatment for refractory/recurrent TN. Optimizing parameters, including DREZ targeting and dual-isocenter strategies, can enhance outcomes, while balancing treatment length to mitigate chronic sensory toxicity. Future research should aim at optimizing treatment parameters to maximize pain relief while minimizing toxicity for these patients.
Keywords: Refractory trigeminal neuralgia; Retreatment; Stereotactic radiosurgery.
© 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of European Society for Radiotherapy and Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Gardner JW. Trigeminal neuralgia: Chapter i. Neurosurgery n.d.;15.
-
- Maarbjerg S, Stefano G, Bendtsen L, Cruccu G. Trigeminal neuralgia - diagnosis and treatment. Cephalalgia n.d.;37:648–57. - PubMed
-
- Headache classification committee of the international headache society (ihs) the international classification of headache disorders. Cephalalgia n.d.;38:1–211. - PubMed
-
- Cruccu G, Gronseth G, Alksne J. Aan-efns guidelines on trigeminal neuralgia management. Eur J Neurol n.d.;15:1013–28. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

