Myelin mapping in patients with rheumatoid arthritis-related fatigue: a TBSS-MTR study of integrity
- PMID: 40486072
- PMCID: PMC12145178
- DOI: 10.1093/bjro/tzaf014
Myelin mapping in patients with rheumatoid arthritis-related fatigue: a TBSS-MTR study of integrity
Abstract
Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients frequently report fatigue, which notably diminishes their quality of life. Emerging research points to a correlation between inflammation-induced fatigue and brain structural alterations.
Objectives: This study evaluates the variance in myelin integrity among patients with RA-related fatigue, investigating the potential of magnetization transfer ratio (MTR) as a biomarker, in comparison with healthy controls.
Methods: A prospective cohort analysis was conducted comprised 60 RA patients with fatigue, categorized into active (n = 30) and non-active (n = 30) disease states, alongside 20 healthy controls (HC). A 3 Tesla MRI system was utilized to perform diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and magnetization transfer imaging (MTI) sequences. MTR maps were generated using in-house MATLAB code and co-registered with DTI data using SPM8. These were then analyzed through tract-based spatial statistics (TBSS) with threshold-free cluster enhancement (TFCE) and corrected for multiple comparisons. MTR values were assessed using Randomize from the FSL toolkit, applying a general linear model (GLM) for voxel-wise analysis and TFCE for p-value generation, with family-wise error (FWE) control (P < .05) for multiple comparisons.
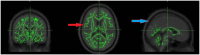
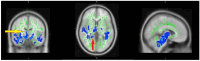
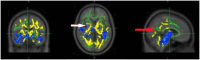
Results: The RF group exhibited significantly lower myelin integrity (TFCE, P < .05) compared to HCs, particularly in the middle cerebellar peduncle and splenium of the corpus callosum, with no marked difference between active and non-active RA disease statuses. There is a discernible disparity in myelin integrity between RA patients with fatigue and healthy individuals, suggesting microstructural white matter alterations that are congruent with DTI findings.
Conclusion: This study reveals that rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients with fatigue exhibit significantly lower myelin integrity, particularly in the middle cerebellar peduncle and splenium of the corpus callosum, compared to healthy controls. Notably, this finding was consistent regardless of the active or non-active status of the RA disease, highlighting persistent white matter alterations in this patents cohort.
Advances in knowledge: The research demonstrates that magnetization transfer ratio (MTR) imaging can effectively map microstructural changes in RA patients with fatigue, suggesting its potential as a biomarker for assessing white matter integrity in this condition. While it does not establish a direct causal relationship, it provides valuable insights into the role of MTR mapping in understanding brain alterations in patients with fatigue-related RA.
Keywords: diffusion tensor imaging; fatigue; magnetization transfer imaging; rheumatoid arthritis; tract-based spatial statistics.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Institute of Radiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interest regarding this work.
Figures
References
-
- Roseira CE, Fittipaldi TR, da Costa LC, da Silva DM, Dias AA, de Figueiredo RM. Good Practices With Injectables: Digital Technology for Nursing Education to Control Infections. SciELO Brasil, 2022. Accessed February 28, 2023. https://www.scielo.br/j/reben/a/dg5ByMXRWf83Jxp7dGCLw3G/ - PMC - PubMed
-
- Piecyk M, Schur P. Neurologic Manifestations of Rheumatoid Arthritis. 2019. (Accessed October 20, 2020). www.uptodate.com
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

