Integration of Network Pharmacology, Transcriptomics, and Metabolomics Strategies to Uncover the Mechanism of Chaihuang Qingfu Pill in Treating Sepsis-Induced Liver Injury
- PMID: 40486124
- PMCID: PMC12144316
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S521626
Integration of Network Pharmacology, Transcriptomics, and Metabolomics Strategies to Uncover the Mechanism of Chaihuang Qingfu Pill in Treating Sepsis-Induced Liver Injury
Abstract
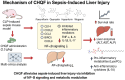
Background: Sepsis is a critical condition triggered by infection and characterized by systemic inflammation and subsequent multiorgan failure. Chaihuang Qingfu Pill (CHQF), an in-hospital formulation developed by Hunan Provincial People's Hospital, is derived from the traditional Chinese medicine compound Qingyi Decoction through optimized herbal compatibility. It possesses pharmacological activities including heat-clearing and purgation, choleretic and anti-jaundice effects, as well as Qi-regulation and mass-resolving properties. Clinically, CHQF is primarily used in the treatment of cholecystitis, pancreatitis, and hepatitis, and has shown potential therapeutic effects in alleviating sepsis-associated liver injury. However, the precise molecular mechanisms and omics-based investigations of CHQF in the context of sepsis remain poorly understood. The NF-κB signaling pathway serves as a central regulatory hub of the inflammatory response. Its activation leads to the excessive expression of pro-inflammatory mediators and cytokines, thereby exacerbating tissue damage and promoting the progression of inflammatory diseases. Consequently, targeting the NF-κB pathway may represent an effective therapeutic strategy for the treatment of sepsis. This study aims to systematically investigate the molecular basis of CHQF in the mitigation of sepsis-associated liver damage.
Purpose: To explore the mechanism of CHQF for the treatment of sepsis-induced liver injury.
Methods: A sepsis mouse model was established via cecal ligation and puncture (CLP). The pharmacological mechanisms of CHQF were explored using network pharmacology, transcriptomics, and metabolomics, which enabled the identification of potential therapeutic targets and pathways, as further validated by in vivo and in vitro experiments.
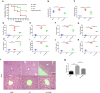
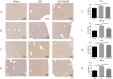
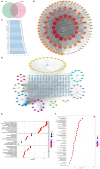
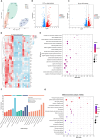
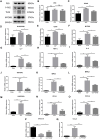
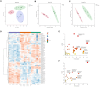
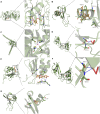
Results: CHQF administration significantly improved the survival rates, reduced systemic inflammation, and restored liver function in CLP-induced sepsis mice, while also mitigating liver tissue injury. Network pharmacological analysis revealed paeoniflorin, quercetin, hyperforin, and wogonin as the core bioactive compounds of CHQF. Transcriptomic profiling identified key targets, including CD14, CXCL2, CCL2, BIRC5, and CXCL8, and demonstrated a significant downregulation of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, IL-17, CCL2, CCL3, CCL4, CXCL2, CXCL3, and CXCL5, alongside NF-κB signaling pathway inhibition. Metabolomic analysis indicated that CHQF treatment reduced the levels of sepsis-related metabolites, including lysophosphatidylcholine (22:6), lysophosphatidylcholine (18:1), 1-LGPC, and C17-sphinganine.
Conclusion: Collectively, these findings suggest that CHQF alleviates sepsis-induced liver injury by modulating the inflammatory response via NF-κB signaling pathway inhibition. This study provides novel insights into the complex molecular mechanisms underlying the therapeutic effects of CHQF in sepsis and enhances the understanding of the pharmacological actions of traditional Chinese medicine in managing sepsis.
Keywords: NF-κB signaling pathway; liver injury; multi-omics; network pharmacology; sepsis; traditional Chinese medicine.
© 2025 Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chaihuang Qingfu Pills Protect Against Acute Pancreatitis-Associated Acute Lung Injury Through MMP9-NLRP3-Pyroptosis Pathway.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Feb 18;18:2317-2338. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S501531. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 39991664 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation and the mechanism of ShengXian and JinShuiLiuJun decoction in the treatment of silicotic fibrosis: An integrated network pharmacology, life omics, and experimental validation study.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jan 30;337(Pt 2):118909. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118909. Epub 2024 Oct 5. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39369919
-
Integrated network pharmacology and experimental validation to elucidate the mechanism of celastrol in mitigating sepsis-induced acute lung injury in mice.Phytomedicine. 2025 Jun;141:156678. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156678. Epub 2025 Mar 20. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40133025
-
Exploring the Anti-PANoptosis Mechanism of Dachaihu Decoction Against Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Injury: Network Pharmacology, Bioinformatics, and Experimental Validation.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Jan 17;19:349-368. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S495225. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 39839500 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis and treatment strategies of sepsis-induced myocardial injury: modern and traditional medical perspectives.Int J Biol Sci. 2025 May 15;21(8):3478-3504. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.111288. eCollection 2025. Int J Biol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40520010 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wang Z, Liu J, Li F, et al. Mechanisms of Qingyi decoction in severe acute pancreatitis-associated acute lung injury via gut microbiota: targeting the short-chain fatty acids-mediated AMPK/NF-kappaB/NLRP3 pathway. Microbiol Spectr. 2023;11(4):e0366422. doi:10.1128/spectrum.03664-22 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

