IgG4-related lung disease with pulmonary lesions and recurrent pleural effusion: A case of report
- PMID: 40486144
- PMCID: PMC12143773
- DOI: 10.1016/j.radcr.2025.04.028
IgG4-related lung disease with pulmonary lesions and recurrent pleural effusion: A case of report
Abstract
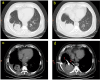
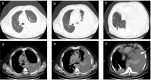
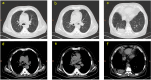
We report a rare case of IgG4-related lung disease (RLD) with pulmonary lesions and recurrent pleural effusion to improve the diagnosis and treatment of this disease. A 60-year-old man was admitted to hospital for cough and dyspnea. CT scan showed a right lower lobe intrapulmonary mass with unilateral right-sided pleural effusion. Histology revealed no malignant findings. After 1 year, the patient re-admitted to our hospital with high serum level of IgG4 and IgE concentrations. CT scan demonstrated partial resolution of intrapulmonary mass and right-sided pleural effusion, while concurrently revealing interval development of substantial left-sided pleural effusion. The patient was diagnosed with IgG4-RLD by biopsy finally. This is a first case report of IgG4-RLD with intrapulmonary lesions accompanied by asynchronous, rapidly accumulating bilateral pleural effusions. Clinicians should consider the possibility of IgG4-RLD with intrapulmonary lesions accompanied by asynchronous, rapidly growing bilateral pleural effusion, particularly after rigorously excluding common diseases.
Keywords: IgG4-related lung disease; Pulmonary lesions; Recurrent pleural effusion.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. on behalf of University of Washington.
Figures

References
-
- Hamano H., Kawa S., Horiuchi A., Unno H., Furuya N., Akamatsu T., et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:732–738. - PubMed
-
- Stone J.H., Zen Y., Deshpande V. IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:539–551. - PubMed
-
- Perugino C.A., Stone J.H. IgG4-related disease: an update on pathophysiology and implications for clinical care. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16:702–714. - PubMed
-
- Mukoyama H., Murakami K., Onizawa H., Shirakashi M., Hiwa R., Tsuji H., et al. A case of atypical IgG4-related disease presenting hypereosinophilia, polyneuropathy, and liver dysfunction. Mod Rheumatol Case Rep. 2023;8:172–177. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

