Staged CBI for Reducing Anxiety and Depression in Lung Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis
- PMID: 40486253
- PMCID: PMC12145106
- DOI: 10.2147/JMDH.S506310
Staged CBI for Reducing Anxiety and Depression in Lung Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis
Abstract
Background: The success rate of Staged cognitive behavioral intervention (CBI) in reducing emotional discomfort and enhancing the life-quality of patients undergoing chemotherapy for lung cancer was assessed retrospectively in this study.
Objective: The records of 55 affected role received/receiving chemotherapy for lung cancer were examined for Staged CBI.
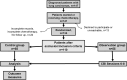
Methods: In this study, patients' life related information's were obtained through demographic questionnaires. The 36-Item Short Form Survey (SF-36) was included as a single question that indicates subjective shifts in well-being. The Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-General (FACT-G) and the Lung Cancer Symptom Scale (LCSS) were designed as measuring scales for quality of life (QoL). Cohen's d indexes were measured to analyze the group's effectual size. The follow-up data were collected 6-8 weeks after the Staged CBI sessions.
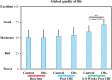
Results: The SF-36 showed that effect size was large for most of the domains (Cohen's d > 1.2) and post CBI intervention was not significant except physical function. The FACT-G survey revealed that improvements were significant for observation group vs control for physical well-being (p = 0.004), social well-being (p = 0.007), emotional well-being (p = 0.008), and functional well-being (p = 0.045). The LCSS survey showed clinically marked changes for activity level, daily routine and social activities from 43.86 ± 20.16 to 71.29 ± 25.42, 45.36 ± 32.65 to 72.36 ± 26.78, and 35.36 ± 31.07 to 77.77 ± 28.58, respectively (P > 0.001). The resulting outcomes were significant in getting better the overall Global QoL of the patients. Besides these, the symptoms burden was also promisingly reduced.
Conclusion: The function of CBI in lung cancer chemotherapy patients has not yet been examined retrospectively. This study investigated how CBI affects the treatment of mental health issues and enhances patients' treatment compliance and quality of life.
Keywords: chemotherapy; lung cancer; retrospective analysis; staged CBI.
© 2025 Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

