Effects of Acupuncture Combined with Conventional Rehabilitation Training for Patients with Post-Stroke Dysphagia: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 40486255
- PMCID: PMC12143297
- DOI: 10.2147/JMDH.S526827
Effects of Acupuncture Combined with Conventional Rehabilitation Training for Patients with Post-Stroke Dysphagia: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Objective: Stroke is a significant global public health challenge. Evidence suggests that acupuncture contributes to the treatment and rehabilitation of post-stroke dysphagia (PSD), effectively improving swallowing function and enhancing patients' quality of life. This study aimed to examine the effects of acupuncture combined with conventional rehabilitation training (CRT) on swallowing function, neurotransmitter levels, nutritional status, and swallowing-related quality of life in patients with PSD.
Methods: Following screening, 90 patients with PSD were randomly assigned to either the intervention group (receiving acupuncture combined with CRT) or the control group (receiving CRT only). Both groups underwent treatment six times per week for four weeks. Primary outcome measures included the standardized swallowing assessment (SSA), the modified Mann assessment of swallowing ability (MMASA), the water swallowing test (WST), and 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) levels. Secondary outcomes assessed swallowing-related quality of life and nutritional indicators.
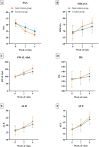
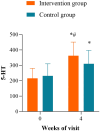
Results: Compared with baseline data, both groups showed improvements after 2 and 4 weeks of treatment, with reductions in SSA scores and increases in MMASA, hemoglobin (HB), albumin (ALB), serum total protein (STP), swallowing quality of life questionnaire (SWAL-QoL) scores, and WST performance. And the intervention group exhibited significantly greater improvements than the control group at the fourth week. Notably, the 5-HT levels in the intervention group were significantly higher than those in the control group after 4 weeks (362.44±88.63 vs 310.16±86.79, P = 0.006).
Conclusion: A 4-week course of acupuncture combined with CRT demonstrated significant benefits in enhancing swallowing function, neurotransmitter levels, nutritional status, and quality of life in patients with PSD.
Keywords: acupuncture; clinical trial; post-stroke dysphagia; rehabilitation training; swallowing function.
© 2025 Xu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest regarding this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Tongnao Huoluo Liyan acupuncture combined with rehabilitation training for post-stroke dysphagia: a randomized controlled trial].Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2025 Apr 12;45(4):435-441. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.20240327-k0004. Epub 2025 Jan 10. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2025. PMID: 40229152 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Efficacy of enhanced dysphagia assessment and dietary intervention in post-stroke dysphagia patients: a randomized controlled study.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2025 May;282(5):2539-2547. doi: 10.1007/s00405-024-09112-y. Epub 2024 Dec 5. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2025. PMID: 39636445 Clinical Trial.
-
[Deep acupuncture of Lianquan (CV23) and Yifeng (TE17) in combination with conventional acupuncture of other acupoints is superior to swallowing rehabilitation training in improving post-stroke dysphagia in apoplexy patients].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2019 Feb 25;44(2):144-7. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.180018. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2019. PMID: 30945493 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Manual Acupuncture or Combination of Rehabilitation Therapy to Treat Poststroke Dysphagia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Oct 15;2022:8803507. doi: 10.1155/2022/8803507. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 36285156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tongue acupuncture for the treatment of post-stroke dysphagia: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Neurosci. 2023 May 25;17:1124064. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1124064. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37304013 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

