Analyzing mechanisms of qing fei bao yuan decoction granules in treating COPD based on LC-MS, network pharmacology and in vivo methods
- PMID: 40486281
- PMCID: PMC12143336
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2024.04.005
Analyzing mechanisms of qing fei bao yuan decoction granules in treating COPD based on LC-MS, network pharmacology and in vivo methods
Abstract
Background and aim: The current therapeutic interventions of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease offer only partial alleviation of symptoms, leaving the majority of patients with persistent and significant clinical manifestations. This investigation seeks to elucidate the underlying pharmacological mechanisms of Qing Fei Bao Yuan Decoction (QFBYD) employing a multidisciplinary approach that includes network pharmacology and molecular docking techniques.
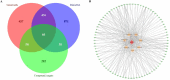
Experimental procedure: The QFBYD formulation were subjected to mass spectrometry analysis, while critical compounds and biological targets were subsequently identified through the TCMSP database. Disease- and drug-specific targets were collated from a plethora of databases, including Batman-TCM, Stitch, Swiss Target Prediction and GeneCards. GO and KEGG pathways were analyzed for the collected targets. A PPI network was constructed using STRING database to isolate core targets. Molecular docking was executed using Auto Dock Tools and PyMOL software, and an animal model of COPD was developed for experimental validation.
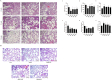
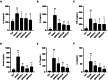
Results and conclusions: Seven salient compounds and five core biological targets were ascertained through our analysis. Additionally, four compounds demonstrated high-affinity binding to the identified targets. Pathways involving bacterial endotoxin response, oxidative stress regulation, and endothelial cell migration were significantly enriched according to the KEGG database. Animal models substantiated that QFBYD ameliorated pathological hallmarks, enhanced respiratory functionality, mitigated overexpression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, augmented the antioxidant defense mechanism, and suppressed the hyperactivity of the five core targets. The efficacy of QFBYD in COPD treatment may be primarily attributed to its role in moderating inflammatory responses and rectifying oxidative imbalances.
Keywords: Chronic obstructive pulmonary emphysema; Experimental analysis; Mechanism; Molecular docking; network pharmacology.
© 2024 Center for Food and Biomolecules, National Taiwan University. Production and hosting by Elsevier Taiwan LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest in the research content.
Figures






Similar articles
-
The Anti-lung Cancer Mechanism of Qingzao Jiufei Decoction was Studied based on Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and Experimental Verification.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2025 Feb 4. doi: 10.2174/0113862073347396241227122956. Online ahead of print. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2025. PMID: 39917915
-
Exploration of the mechanism of Zisheng Shenqi decoction against gout arthritis using network pharmacology.Comput Biol Chem. 2021 Feb;90:107358. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2020.107358. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Comput Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33243703 Review.
-
Mechanism of Action of Bu-Fei-Yi-Shen Formula in Treating Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Based on Network Pharmacology Analysis and Molecular Docking Validation.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Nov 26;2020:9105972. doi: 10.1155/2020/9105972. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 33313323 Free PMC article.
-
Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation of Jinwei Decoction for Enhancement of Glucocorticoid Anti-Inflammatory Effect in COPD through miR-155-5p.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2025;28(2):351-370. doi: 10.2174/0113862073279344240215050056. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2025. PMID: 39279134
-
Network pharmacology prediction and molecular docking-based strategy to explore the potential mechanism of Huanglian Jiedu Decoction against sepsis.Comput Biol Med. 2022 May;144:105389. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105389. Epub 2022 Mar 9. Comput Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 35303581 Review.
References
-
- MacLeod M., Papi A., Contoli M., et al. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbation fundamentals: diagnosis, treatment, prevention and disease impact. Respirology. 2021;26(6):532–551. - PubMed
-
- Cazzola M., Matera M.G. The effect of doxofylline in asthma and COPD. Respir Med. 2020;164:105904. - PubMed
-
- Peng T., Qi B., He J., Ke H., Shi J. Advances in the development of phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2020;63(19):10594–10617. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
