Management of Patients With COVID-19 During the Pandemic: A Retrospective Cohort Study From a Tertiary Care Centre in Mumbai, India
- PMID: 40486438
- PMCID: PMC12144663
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.83711
Management of Patients With COVID-19 During the Pandemic: A Retrospective Cohort Study From a Tertiary Care Centre in Mumbai, India
Abstract
Introduction: We conducted the present analysis to understand the clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19 infection and the factors associated with mortality over the one-and-a-half years of the pandemic in Mumbai, India.
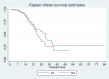
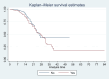
Methods: This is a retrospective cohort study of 3561 COVID-19 patients admitted to a private tertiary care hospital in Mumbai, India. The main outcome variable for analysis was death (yes/no). We compared the characteristics of COVID-19 patients who had died during their stay in the hospital with those who had not died. We used survival analysis to identify the factors associated with mortality.
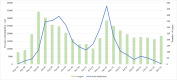
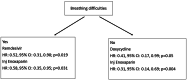
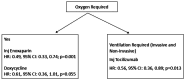
Results: The mortality rate was 0.71 per 100 person-days (95% CI: 0.61-0.81 per 100 person days (PD)); it was higher (2.03 (95% CI: 1.47, 2.82) per 100 PD) in those aged >= 80 years compared with 18-39 years (p<0.001). The hazard rate (HR) was significantly higher in those with chronic liver disease (HR: 5.12, 95% CI: 1.78, 14.71; p=0.002) and lower in those who were treated with injection enoxaparin (HR: 0.46, 95% CI: 0.31, 0.69; p<0.001). In patients without breathing difficulties, the hazard was significantly lower in those treated with doxycycline (HR: 0.41, 95% CI: 0.17, 0.99; p=0.05). In patients who presented with breathing difficulties, hazard was significantly lower in those who were treated with remdesivir (HR: 0.52, 95% CI: 0.31, 0.90; p=0.019). In patients who required ventilatory support (invasive and non-invasive), the hazard was significantly lower with injected tocilizumab (HR: 0.56, 95% CI: 0.36, 0.89; p=0.013).
Conclusions: The mortality was highest during the initial days of the pandemic and in patients with co-morbidities. Remdesivir and the tocilizumab injection were useful in the reduction of mortality in the severe form of COVID-19 infection. Doxycycline was useful in milder and less severe forms of infection. However, enoxaparin injection was associated with lower mortality in most of these cases.
Keywords: clinical experience; cohort; covid-19; doxycycline; enoxaparin; mortality; remdesivir; tocilizumab.
Copyright © 2025, Tulara et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Ethics Committee of Dr. L H Hiranandani Hospital issued approval Reference # DRLHH/EC/2023/15. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures





References
-
- Listings of WHO’s Response to COVID-19. [ Feb; 2024 ]. 2023. https://www.who.int/news/item/29-06-2020-covidtimeline https://www.who.int/news/item/29-06-2020-covidtimeline
-
- Naming the Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) and the Virus That Causes It. [ Feb; 2024 ]. 2024. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/technica... https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/technica...
-
- Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Directorate General of Health Services. [ Feb; 2024 ]. 2023. https://ghp.py.gov.in/sites/default/files/guidelines-be-followed-detecti... https://ghp.py.gov.in/sites/default/files/guidelines-be-followed-detecti...
-
- India Fights Corona COVID-19: Government of India. [ Feb; 2024 ]. 2023. https://www.mygov.in/covid-19/ https://www.mygov.in/covid-19/
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
