Biological mechanisms of pulmonary inflammation and its association with seropositive rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 40486510
- PMCID: PMC12141282
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1530753
Biological mechanisms of pulmonary inflammation and its association with seropositive rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
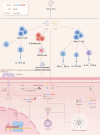
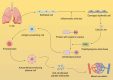
Although the pathogenesis of seropositive rheumatoid arthritis (RA) remains unclear, studies suggest that pulmonary inflammation-related biological mechanisms play a significant role in its development. This review thoroughly explores the mechanisms underlying early pulmonary lesions in seropositive RA, focusing on the mucosal barrier hypothesis, neutrophil extracellular traps, pathogenic microbial infections like COVID-19, Vitamin D, the microbiome and gut-lung axis, inhalation exposures and chronic pulmonary diseases. This study seeks to provide novel insights and theoretical foundations for the prevention and treatment of seropositive rheumatoid arthritis.
Keywords: COVID-19; anti-citrullinated protein antibodies; gut-lung axis; pulmonary inflammation; rheumatoid arthritis.
Copyright © 2025 Yang, Song and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Indoxyl sulfate (IS) mediates pro-inflammatory responses in severe pneumonia in patients with rheumatoid arthritis associated interstitial lung disease.Clin Immunol. 2025 Mar;272:110430. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2025.110430. Epub 2025 Jan 26. Clin Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39875062
-
Linking microbial communities to rheumatoid arthritis: focus on gut, oral microbiome and their extracellular vesicles.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 16;16:1503474. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1503474. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40308573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibodies Are Associated With Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in the Sputum in Relatives of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017 Jun;69(6):1165-1175. doi: 10.1002/art.40066. Epub 2017 May 2. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 28182854 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Tied to Rheumatoid Arthritis: Points to Ponder.Front Immunol. 2021 Jan 29;11:578129. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.578129. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33584645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lung inflammation in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis.Immunol Rev. 2020 Mar;294(1):124-132. doi: 10.1111/imr.12842. Epub 2020 Feb 6. Immunol Rev. 2020. PMID: 32030763 Review.
References
-
- Mena-Vazquez N, Perez AL, Manrique-Arija S, Romero BC, Gomez CC, Urena GI, et al. . Analysis of clinical-analytical characteristics in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and interstitial lung disease: case-control study. Reumatol Clin (Engl Ed). (2021) 17:197–202. doi: 10.1016/j.reuma.2019.06.001 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Giles JT, Danoff SK, Sokolove J, Wagner CA, Winchester R, Pappas DA, et al. . Association of fine specificity and repertoire expansion of anticitrullinated peptide antibodies with rheumatoid arthritis associated interstitial lung disease. Ann Rheum Dis. (2014) 73:1487–94. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-203160 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

