Targeting interleukin-1 signaling for renoprotection
- PMID: 40486517
- PMCID: PMC12141784
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1591197
Targeting interleukin-1 signaling for renoprotection
Abstract
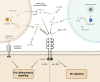
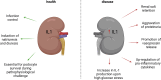
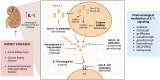
Sterile inflammation with ensuing immune-mediated kidney damage has been implicated in pathophysiology of acute and chronic kidney diseases. Disinhibition of interleukin 1 (IL-1) signaling triggers local inflammation of renal tissue and may initiate or aggravate systemic inflammatory response. The IL-1α isoform is released by many cell types during cell necrosis to attract immune cells, whereas the IL-1β isoform is secreted by immune cells to amplify local inflammatory responses. The unfolding of IL-1 signaling is restricted by an endogenous IL-1 receptor antagonist and a decoy IL-1 receptor variant. Pharmacological IL-1 inhibitors mimicking the natural IL-1 suppressors are instrumental in management of a broad spectrum of (auto)inflammatory disorders. Progression of several kidney diseases toward renal fibrosis has been associated with a disbalance between the pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory IL-1 signaling components. While IL-1 inhibitors have proven success in prevention and treatment of renal complications accompanying the autoimmune disorders, broader opportunities in kidney diseases have been expected. The present review work analyzes potential niches for IL-1 signaling in the field of nephrology.
Keywords: ADPKD (autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease); acute kidney injury; chronic kidney disease; cytokines; interleukins; nephroprotection.
Copyright © 2025 Bogdanova, Samsonov, Lebedeva, Bukhanova, Materenchuk and Mutig.
Conflict of interest statement
MS and DBu are employed by R-Pharm. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting inerleukin-6 for renoprotection.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 11;15:1502299. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1502299. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39723211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifactorial functions of the inflammasome component NLRP3 in pathogenesis of chronic kidney diseases.Kidney Int. 2019 Jul;96(1):58-66. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2019.01.014. Epub 2019 Mar 4. Kidney Int. 2019. PMID: 30922667 Review.
-
The interleukin (IL)-1 cytokine family--Balance between agonists and antagonists in inflammatory diseases.Cytokine. 2015 Nov;76(1):25-37. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2015.06.017. Epub 2015 Jul 13. Cytokine. 2015. PMID: 26185894 Review.
-
Interleukin-1 receptor activation aggravates autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease by modulating regulated necrosis.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019 Aug 1;317(2):F221-F228. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00104.2019. Epub 2019 May 29. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31141402 Free PMC article.
-
The NLRP3 inflammasome in kidney disease and autoimmunity.Nephrology (Carlton). 2016 Sep;21(9):736-44. doi: 10.1111/nep.12785. Nephrology (Carlton). 2016. PMID: 27011059 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of NLRP3 Inflammasome in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Macrovascular Complications.J Clin Med. 2025 Jun 29;14(13):4606. doi: 10.3390/jcm14134606. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40648980 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

