Serum peptides as candidate biomarkers for relapsing polychondritis
- PMID: 40486527
- PMCID: PMC12143761
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmsacl.2025.04.001
Serum peptides as candidate biomarkers for relapsing polychondritis
Abstract
Introduction: Relapsing polychondritis (RP) is an intractable disease characterized by recurrent inflammation of cartilaginous tissue throughout the body. It is difficult to accurately diagnose RP, and no useful biomarkers have yet been identified.
Objectives: We analyzed serum peptide profiles to identify novel candidate biomarkers for RP.
Methods: Thirty-seven patients with RP, 42 patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and 35 healthy control (HC) subjects were divided into training and testing sets. Seven patients demonstrating granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) were used for validation. The ion intensity of serum peptides was comprehensively measured by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight/time-of-flight mass spectrometry and applied to a supervised multivariate analysis. Peptides of interest were analyzed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.
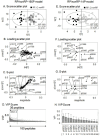
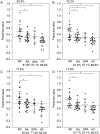
Results: In the training set, models developed based on 11 (RP/HC-11P model), 9 (RP/RA-9P model), and 14 (RP/nonRP-14P model) peptides, out of 160 peptides detected were able to completely discriminate the RP group from the HC, RA, and nonRP (HC + RA) groups. Almost all of the 15 identified discriminatory peptides comprising these models were fragments of proteins associated with coagulation. Four models, each consisting of 4 out of 10 identified peptides of the RP/nonRP-14P model (models RP/nonRP-4P-2, -10, -11, and -38), provided ≥ 70.0 % sensitivity and specificity when applied to the validation set (the testing set and the GPA group) (AUROC, 0.779-0.815). Notably, the RP/nonRP-4P-2 model provided 83.3 % sensitivity and 71.7 % specificity in the validation set (AUROC, 0.802).
Conclusions: Serum peptides are useful as candidate biomarkers for discriminating RP and may be involved in the pathophysiology of RP.
Keywords: Biological markers; Mass spectrometry; Relapsing polychondritis; Serum peptides.
© 2025 THE AUTHORS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- McAdam L.P., O'Hanlan M.A., Bluestone R., Pearson C.M. Relapsing polychondritis: prospective study of 23 patients and a review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 1976;55(3):193–215. - PubMed
-
- Damiani J.M., Levine H.L. Relapsing polychondritis–report of ten cases. Laryngoscope. 1979;89:929–946. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

