APOE genetic variability in an Egyptian cohort of PD
- PMID: 40486732
- PMCID: PMC12141286
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1579968
APOE genetic variability in an Egyptian cohort of PD
Abstract
Background: The apolipoprotein E (APOE) gene, encompassing three alleles (ε2, ε3, ε4), is a critical player in lipid metabolism and has been extensively studied for its role in neurodegenerative diseases. This study examines APOE genetic variability and its association with PD in an Egyptian cohort.
Methods: A total of 891 participants, including 422 PD patients and 469 healthy controls, were included in this study. APOE genotyping was performed using Kompetitive Allele Specific PCR (KASP) to detect the rs429358 and rs7412 SNPs, which define the APOE alleles. APOE alleles were categorized based on the genotypes into ε2, ε3, and ε4 groups. Clinical assessments of PD patients included age at onset, disease severity (MDS-UPDRS), and demographic factors. Statistical analyses compared APOE distributions between PD and control groups and examined associations with clinical variables.
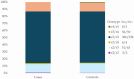
Results: The ε3 allele was the most prevalent in the cohort (77.3%), aligning with global and African trends. The ε2 allele was observed in 11.4%, and the ε4 allele in 11.3%, with both frequencies being lower than reported African estimates. The ε3/ε3 genotype was predominant in both PD patients (72.51%) and controls (72.07%). The ε4/ε4 genotype was absent in PD cases and rare among controls (0.64%). No significant association was found between APOE genotypes and PD risk, age at onset, or disease severity.
Conclusion: Our findings do not support a significant role for APOE in PD susceptibility or severity in Egyptians.
Keywords: APOE; Egyptian; KASP; Parkinson’s disease; genetics.
Copyright © 2025 Khedr, William, Elhosseiny, Shalash, Fawi, Yousef, El-Jaafary, Lee, Jama, Koraym, Helmy, Salah, George, Haridy, Nabhan, Atputhavadivel, Elfarrash, Ragab, Hegazy, Elsaid, Gabr, Shebl, Aly, Abdelwahhab, Belal, Elsayed, El-Gamal, Elgamal, Ragab, Mekky, Houlden, Rizig and Salama.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Arafa S., Abdelsalam S., El-Gilany A. H., Mosaad Y. M., Abdel-Ghaffar A. (2018). Endothelial nitric oxide synthase Glu 298 asp (G894T) and apolipoprotein E gene polymorphism as possible risk factors for coronary heart disease among Egyptians. Egyptian Heart J 70, 393–401. doi: 10.1016/j.ehj.2018.08.001, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

