Unlocking the potential of wearable technology: Fitbit-derived measures for predicting ADHD in adolescents
- PMID: 40487008
- PMCID: PMC12142065
- DOI: 10.3389/frcha.2025.1504323
Unlocking the potential of wearable technology: Fitbit-derived measures for predicting ADHD in adolescents
Abstract
Background: Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a common neurodevelopmental disorder with a complex etiology. The current diagnostic process for ADHD is often time-intensive and subjective. Recent advancements in machine learning offer new opportunities to improve ADHD diagnosis using diverse data sources. This study explores the potential of Fitbit-derived physical activity data to enhance ADHD diagnosis.
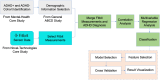
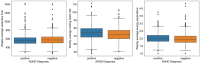
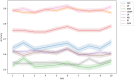
Method: We analyzed a sample of 450 participants from the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) study (data release 5.0). Correlation analyses were conducted to examine associations between ADHD diagnosis and Fitbit-derived measurements, including sedentary time, resting heart rate, and energy expenditure. We then used multivariable logistic regression models to evaluate the predictive power of these measurements for ADHD diagnosis. Additionally, machine learning classifiers were trained to automatically classify individuals into ADHD+ and ADHD- groups.
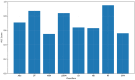
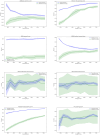
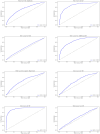
Results: Our correlation analyses revealed statistically significant associations between ADHD diagnosis and Fitbit-derived physical activity data. The multivariable logistic regression models identified specific Fitbit measurements that significantly predicted ADHD diagnosis. Among the machine learning classifiers, the Random Forest outperformed others with cross-validation accuracy of 0.89, AUC of 0.95, precision of 0.88, recall of 0.90, F1-score of 0.89, and test accuracy of 0.88.
Conclusion: Fitbit-derived measurements show promise for predicting ADHD diagnosis, with machine learning classifiers, particularly Random Forest, demonstrating high predictive accuracy. These findings suggest that wearable data may contribute to more objective and efficient methods for ADHD identification, potentially enhancing clinical practices for diagnosis and management.
Keywords: ADHD; adolescent mental health; fitbit-derived physical activity; machine learning; wearable technology.
© 2025 Rahman.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Varrasi S, Boccaccio FM, Guerrera CS, Platania GA, Pirrone C, Castellano S. Schooling and occupational outcomes in adults with ADHD: predictors of success and support strategies for effective learning. Educ Sci (Basel). (2022) 13(1):37. 10.3390/educsci13010037 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

