Metabolites and coronary heart disease: A two sample Mendelian randomization
- PMID: 40487072
- PMCID: PMC12141869
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijcrp.2025.200365
Metabolites and coronary heart disease: A two sample Mendelian randomization
Abstract
Background: In observational studies, circulating metabolites were related to Coronary heart disease (CHD), but their causal relationship is unknown. In this study, we sought to determine a bidirectional causal relationship between circulating metabolites and CHD and to explore whether circulating metabolites are associated with a decreased risk of CHD.
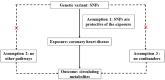
Methods: In our two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) study, the top SNPs associated with circulating metabolites (n = 24, 925) as well as CHD (n = 86, 995) were acquired from publicly available genome-wide association studies (GWAS). The SNPs estimates were pooled using inverse variance weighted meta-analysis, with median weighted by sensitivity analyses, MR Egger and MR Pleiotropy Residual Sum and Outlier (PRESSO).
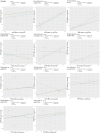
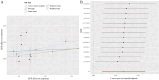
Results: Free cholesterol in large LDL(p, 6.9E-07; OR, 2.2; 95%CI,1.6-3.0),total cholesterol in medium LDL(p, 1.0E-06; OR, 1.8; 95%CI,1.4-2.3)Total cholesterol in LDL (p,1.43083E-05; OR,1.7; 95%CI, 1.3-2.2). Phospholipids in medium LDL (p,0.0; OR,1.6; 95%CI, 1.2-2.1); Total cholesterol in small VLDL (p,0.0; OR, 1.8; 95%CI, 1.2-2.7); Triglycerides in small VLDL (p,0.0, OR, 1.3; 95%CI, 1.0-1.6); Free cholesterol in small VLDL (p,0.0; OR,1.3; 95%CI, 1.0-1.7); Phospholipids in small VLDL (p,0.0; OR,1.3, 95%CI,1.0-1.7); Triglycerides in small HDL (p,0.0, OR,1.3,95%CI,1.0-1.7); Alanine (0.0, OR,1.2,95%CI,1.0-1.6) were positively associated with CHD. Phospholipids in medium HDL (p,0.0, OR,0.8; 95%CI, 0.6-0.9) might have a protective effect on CHD, which were negatively associated with CHD.
Conclusions: Our MR analysis demonstrated a protective effect of Phospholipids in medium HDL, and a potentially anti-protective effect of Free cholesterol in large LDL, Total cholesterol in medium LDL, Total cholesterol in LDL, Phospholipids in medium LDL, Total cholesterol in small VLDL, Triglycerides in small VLDL, Free cholesterol in small VLDL, Phospholipids in small VLDL, Triglycerides in small HDL, Alanine on the pathogenesis of CHD. Additional studies are required to translate the findings into practice.
Keywords: Coronary heart disease; Mendelian randomization; Metabolites.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
