Integrating gene demethylation and immune modulation: PD-1 nanovesicles as a dual-action therapy for NSCLC
- PMID: 40487169
- PMCID: PMC12145548
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.101851
Integrating gene demethylation and immune modulation: PD-1 nanovesicles as a dual-action therapy for NSCLC
Abstract
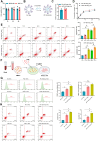
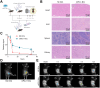
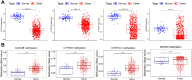
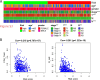
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) remains a formidable challenge in oncology, underscoring the urgent need for innovative therapeutic strategies. This study explores the potential of PD-1-modified multifunctional nanovesicles (NVs) loaded with 5-azacytidine (5-Aza) for NSCLC treatment. By integrating bioinformatics analyses with in vitro and in vivo experiments, methylation-driven genes closely associated with NSCLC progression and prognosis-CLEC3B, CYP27A1, CYP4B1, and NR0B2-were identified. Functional assays revealed that 5-Aza effectively demethylates these genes, reducing NSCLC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. PD-1-modified NVs demonstrated precise targeting of NSCLC cells via PD-L1 binding, while the combination of PD-1 NVs and 5-Aza synergistically enhanced peripheral blood mononuclear cell activation, induced apoptosis, and amplified anti-tumor immunity. In vivo, studies confirmed the tumor-targeting ability and significant therapeutic efficacy of PD-1 NVs. This synergistic strategy of epigenetic modulation and immune activation offers a promising avenue for NSCLC management. These findings contribute valuable insights into developing targeted nanotherapeutics for effective NSCLC treatment.
Keywords: 5-Azacytidine; Epigenetic therapy; Immune activation; Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); PD-1-Modified nanovesicles.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Genetically engineered PD-1 displaying nanovesicles for synergistic checkpoint blockades and chemo-metabolic therapy against non-small cell lung cancer.Acta Biomater. 2023 Apr 15;161:184-200. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2023.03.002. Epub 2023 Mar 7. Acta Biomater. 2023. PMID: 36893957
-
ILT4 inhibition prevents TAM- and dysfunctional T cell-mediated immunosuppression and enhances the efficacy of anti-PD-L1 therapy in NSCLC with EGFR activation.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 19;11(7):3392-3416. doi: 10.7150/thno.52435. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33537094 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations of immune response of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Azacytidine.Oncotarget. 2013 Nov;4(11):2067-79. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1542. Oncotarget. 2013. PMID: 24162015 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Pathway, Yes-Associated Protein (YAP) and the Regulation of Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC).Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 5;20(15):3821. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153821. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31387256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single or combined immune checkpoint inhibitors compared to first-line platinum-based chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab for people with advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Dec 14;12(12):CD013257. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013257.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 30;4:CD013257. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013257.pub3. PMID: 33316104 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Wang Z.-H., Ye L.-L., Xiang X., Wei X.-S., Niu Y.-R., Peng W.-B., Zhang S.-Y., Zhang P., Xue Q.-Q., Wang H.-L., Du Y.-H., Liu Y., Ai J.-Q., Zhou Q. Circular RNA circFBXO7 attenuates non-small cell lung cancer tumorigenesis by sponging miR-296-3p to facilitate KLF15-mediated transcriptional activation of CDKN1A. Transl. Oncol. 2023;30 doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2023.101635. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Isomoto K., Haratani K., Tsujikawa T., Makutani Y., Kawakami H., Takeda M., Yonesaka K., Tanaka K., Iwasa T., Hayashi H., Ito A., Nishio K., Nakagawa K. Mechanisms of primary and acquired resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors in advanced non–small cell lung cancer: a multiplex immunohistochemistry–based single-cell analysis. Lung Cancer. 2022;174:71–82. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2022.10.012. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

