Pan-genome analysis of the R2R3-MYB genes family in Brassica napus unveils phylogenetic divergence and expression profiles under hormone and abiotic stress treatments
- PMID: 40487211
- PMCID: PMC12141308
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1588362
Pan-genome analysis of the R2R3-MYB genes family in Brassica napus unveils phylogenetic divergence and expression profiles under hormone and abiotic stress treatments
Abstract
Introduction: The R2R3-MYB transcription factors (TFs) are pivotal regulators of plant growth, development, and stress responses. However, their genetic diversity and functional roles in Brassica napus remain underexplored at a pan-genome scale.
Methods: We identified R2R3-MYB genes in 18 published rapeseed genomes and analyzed their genomic distribution patterns, gene duplication, selective pressure, gene structure, conserved motifs, and phylogenetic relationships using a pan-genome approach. Additionally, transcriptomic datasets from hormone treatments and drought/heat stress experiments were analyzed to identify hormone-responsive and stress-responsive genes.
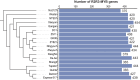
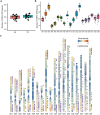
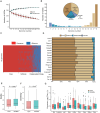
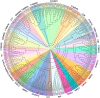
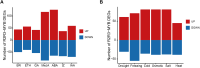
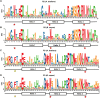
Results: We systematically identified 7,552 R2R3-MYB genes from 18 B. napus genomes, which were grouped into 353 gene clusters based on the pan-genome approach, including 139 core, 121 softcore, 68 dispensable, and 25 private gene clusters. Similar to Arabidopsis, the B. napus R2R3-MYB genes can be clustered into 29 subgroups based on the phylogenetic tree, suggesting conserved functional roles in B. napus and A. thaliana. Cis-element profiling highlighted enrichment in hormone-responsive and stress-related elements in the promoter regions of the R2R3-MYB genes. Transcriptomic analyses identified 283 hormone-responsive and 266 stress-responsive R2R3-MYB genes, and 30 co-regulated genes under drought and heat stress implicate their roles in combined stress adaptation.
Discussion: These findings provide the first pan-genome resource for R2R3-MYB genes in B. napus, which can serve as pivotal targets for enhancing stress resilience in rapeseed breeding programs.
Keywords: R2R3-MYB; abiotic stresses; pan-genome analysis; phylogenetic relationship; plant hormones.
Copyright © 2025 Fan, Li, Huang, Liang, Jing, Li, Yang, Liu and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

