Ascorbic Acid Prevents Efavirenz-Induced Anxiety-Like Behavior and Brain Oxidative Stress in Zebrafish
- PMID: 40487383
- PMCID: PMC12145930
- DOI: 10.1155/omcl/8867221
Ascorbic Acid Prevents Efavirenz-Induced Anxiety-Like Behavior and Brain Oxidative Stress in Zebrafish
Abstract
Efavirenz (EFV) is a medication widely used for the treatment of HIV-positive patients. Several studies have demonstrated that the prolongate use of EFV can lead to the development of neurological diseases, such as panic syndrome, depression, and anxiety disorders. In this current study, we evaluate whether the ascorbic acid (AA) treatment can prevent anxiety-like behavior and brain oxidative stress induced by EFV treatment in zebrafish. Our data demonstrated that the EFV treatment induces anxiogenic-like behavior and intense lipid peroxidation in the zebrafish brain. The AA treatment was able to prevent both anxiogenic-like behavior and brain oxidative stress elicited by the EFV treatment. Therefore, our data provide robust evidence that the EFV induced anxiety-like behavior in zebrafish via a redox-dependent pathway and that AA treatment can minimize these adverse effects. Taken together, our preclinical study strongly suggests that the use of an AA-enriched diet can minimize the effects of EFV on the central nervous system (CNS) and improve the quality of life for patients undergoing EFV treatment.
Keywords: anxiety-like behavior; ascorbic acid; efavirez; oxidative stress; zebrafish.
Copyright © 2025 Emerson Feio Pinheiro et al. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
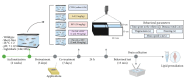
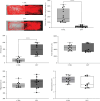
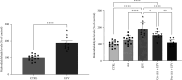
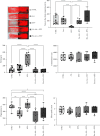
References
-
- WHO. Global Health Sector Strategy on HIV 2016-2021. 2016.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

