Effects of different levels of physical activity on the health-related quality of life among rural junior high school students in China: the moderating role of parental co-participation in physical activities
- PMID: 40487525
- PMCID: PMC12141325
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1556246
Effects of different levels of physical activity on the health-related quality of life among rural junior high school students in China: the moderating role of parental co-participation in physical activities
Abstract
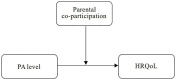
Background: Health benefits are associated with physical activity (PA) and PA levels. This study aims to explore the impact of PA levels (low, moderate, high) on health-related quality of life (HRQoL) among rural junior high school students in China, as well as the moderating role of parental co-participation in physical activities.
Methods: A stratified cluster sampling method was used to select 1,440 junior high school students from rural areas in southwest China. A total of 1,181 students completed the questionnaire, with a completion rate of 82.0%, including 608 boys (51.45%). HRQoL was measured using the Chinese version of the PedsQL 4.0, and PA levels was analyzed using the IPAQ-SF. T-tests, chi-square tests, linear regression, and two-way ANOVA were used for statistical analysis.
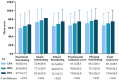
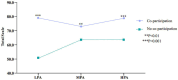
Results: The results showed that 81.8% of rural junior high school students participated in moderate PA and high PA, with 82.3% of boys and 81.2% of girls. In both unadjusted and adjusted models, compared to low PA, students participating in moderate PA and high PA had significantly higher HRQoL scores in all dimensions, summary scales, and total scales, with the high PA showing particularly higher scores. Parental co-participation significantly moderated the relationship between PA and HRQoL (F = 13.569, p < 0.001), and the moderating effect was significant at every PA level, especially at high PA here the effect was most prominent.
Conclusion: Physical activity has a significant positive impact on HRQoL of rural junior high school students, with higher PA levels leading to more significant improvements in all HRQoL dimensions, summary scales, and total scales. Parental co-participation enhances the positive effect of PA on the HRQoL of rural junior high school students, particularly at the high PA, where the moderating effect is more pronounced. Parental co-participation, through the provision of social support, emotional reinforcement, and behavioral modeling, significantly enhances adolescents' intrinsic motivation to participate in physical activity, and further augments its salutary effects on their physical and psychological well-being. This study provides empirical support for health promotion among rural adolescents.
Keywords: China; health-related quality of life; parental co-participation; physical activity; rural junior high school students.
Copyright © 2025 Yang, Zhao, Gao, Guo, Jia and Białas.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Julián-Almarcegui C, Gómez-Cabello A, Huybrechts I, GonzálezAguero A, Kaufman JM, Casajus JA, et al. . Combined effects of interaction between physical activity and nutrition on bone health in children and adolescents: a systematic review. Nutr Rev. (2015) 73:127–39. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuu065, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical