Comparisons of various insulin resistance indices for new-onset metabolic syndrome before midlife: The CHIEF cohort study, 2014-2020
- PMID: 40487604
- PMCID: PMC12142194
- DOI: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i5.101840
Comparisons of various insulin resistance indices for new-onset metabolic syndrome before midlife: The CHIEF cohort study, 2014-2020
Abstract
Background: Some non-insulin-based insulin resistance (IR) indices have been found to be associated with metabolic syndrome (MetS); however, few cohort studies have compared the capacities of these indices for predicting incident MetS in young adults.
Aim: To investigate the associations of various non-insulin-based IR (NI-IR) indices with new-onset MetS in young military personnel.
Methods: A total of 2890 armed forces personnel in Taiwan who were aged 18-39 years and did not have MetS at baseline were followed to monitor the incidence of new-onset MetS from 2014 to the end of 2020. Six NI-IR indices, including the metabolic score for IR (METS-IR), triglyceride (TG)-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) ratio, TG glucose (TyG) index, Zhejiang University (ZJU) index, total cholesterol (TC)-to-HDL-C ratio, and alanine transaminase (ALT)-to-aspartate transaminase (AST) ratio, were defined according to specific criteria. Incident MetS was identified on the basis of each annual health examination using the International Diabetes Federation criteria. Multiple Cox regression analyses were conducted, adjusting for age, sex, waist circumference, smoking status, alcohol consumption status, and physical activity, to assess the associations of the NI-IR indices with incident MetS. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) was used to compare the capacities of these NI-IR indices for predicting new-onset MetS.
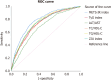
Results: During a median follow-up of 5.8 years, there were 673 patients with new-onset MetS (23%). All six of the NI-IR indices were significantly and positively associated with incident MetS. In the entire cohort, the greatest AUROC was found for the METS-IR [0.782; 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.762-0.801; all P values compared to the other NI-IR indices < 0.05], followed by the TG/HDL-C ratio (0.752; 95%CI: 0.731-0.772), ZJU index (0.743; 95%CI: 0.722-0.764), TyG index (0.734; 95%CI: 0.713-0.756), TC/HDL-C ratio (0.731; 95%CI: 0.709-0.752), and then the ALT/AST ratio (0.734; 95%CI: 0.713-0.756).
Conclusion: This study suggests that almost all the NI-IR indices are associated with the development of MetS in military young adults. The METS-IR is the strongest predictor of new-onset MetS before midlife.
Keywords: Cohort study; Insulin resistance indices; Metabolic syndrome; Young adults.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All authors declared to have no conflict of interest for this article.
Figures
References
-
- Ding C, Yang Z, Wang S, Sun F, Zhan S. The associations of metabolic syndrome with incident hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease: a cohort study. Endocrine. 2018;60:282–291. - PubMed
-
- Demir M, Lang S, Steffen HM. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease - current status and future directions. J Dig Dis. 2015;16:541–557. - PubMed
-
- Gluvic Z, Zaric B, Resanovic I, Obradovic M, Mitrovic A, Radak D, Isenovic ER. Link between Metabolic Syndrome and Insulin Resistance. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2017;15:30–39. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

