Exercise training benefits pancreatic islet by modulating the insulin-like growth factor 1/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway
- PMID: 40487621
- PMCID: PMC12142207
- DOI: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i5.101447
Exercise training benefits pancreatic islet by modulating the insulin-like growth factor 1/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway
Abstract
Background: Diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance as well as impaired insulin production, with β-cell dysfunction playing a critical role in disease progression. Exercise is known to improve insulin sensitivity, but its effects on pancreatic islet quality and function remain poorly understood. This work hypothesized that swimming training enhances glycemic control and insulin secretion by upregulating the insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1)/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B (PI3K/AKT) pathway in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats.
Aim: To investigate the effects of swimming on pancreatic islet quality and function in STZ-induced diabetic rats via the IGF-1/PI3K/AKT pathway.
Methods: Twenty-six Sprague-Dawley rats were grouped into diabetic and control groups, with each group further split into exercise and sedentary subgroups. Diabetic rats were induced with STZ. The exercise groups underwent swimming training for 60 minutes/day, 5 days/week, for 8 weeks. Body weight, food intake, blood glucose, insulin, lipids, and muscle glycogen were measured. Pancreatic islet morphology and the protein expression levels of IGF-1, PI3K, and AKT were analyzed. Data were analyzed using two-way repeated-measure ANOVA, followed by Tukey's post-hoc test.
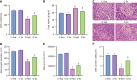
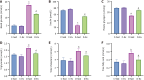
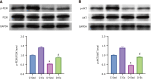
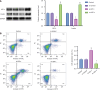
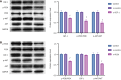
Results: Exercise training significantly improved body weight [diabetic exercise group (D-Ex): 390.66 ± 50.14 g vs diabetic sedentary group (D-Sed): 315.89 ± 50.12 g, P < 0.05], reduced blood glucose (D-Ex: 12.21 ± 4.43 mmol/L vs D-Sed: 17.79 ± 2.05 mmol/L, P < 0.05), and increased insulin levels (D-Ex: 53.50 ± 15.31 pmol/L vs D-Sed: 25.31 ± 10.23 pmol/L, P < 0.05) in diabetic rats. It also enhanced islet morphology, increased IGF-1 expression, and activated the PI3K/AKT pathway (P < 0.05). In-vitro experiments confirmed that IGF-1 positively regulated insulin expression and inhibited β-cell apoptosis via the PI3K/AKT pathway.
Conclusion: Exercise training improves pancreatic islet quality and function in diabetic rats by modulating the IGF-1/PI3K/AKT pathway, highlighting its therapeutic potential for diabetes management.
Keywords: Diabetes; Exercise training; Insulin-like growth factor 1; Islet; Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures
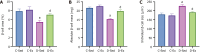

References
-
- Wajchenberg BL. beta-cell failure in diabetes and preservation by clinical treatment. Endocr Rev. 2007;28:187–218. - PubMed
-
- Qian L, Xu L, Wang X, Fu X, Gu Y, Lin F, Peng Y, Li G, Luo M. Early insulin secretion failure leads to diabetes in Chinese subjects with impaired glucose regulation. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2009;25:144–149. - PubMed
-
- Park S, Hong SM, Lee JE, Sung SR. Exercise improves glucose homeostasis that has been impaired by a high-fat diet by potentiating pancreatic beta-cell function and mass through IRS2 in diabetic rats. J Appl Physiol (1985) 2007;103:1764–1771. - PubMed
-
- Min HK. Non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) in Korea. Diabet Med. 1996;13:S13–S15. - PubMed
-
- Weir GC, Bonner-Weir S. Five stages of evolving beta-cell dysfunction during progression to diabetes. Diabetes. 2004;53 Suppl 3:S16–S21. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

