Neurophysiological mechanisms of electroacupuncture in regulating pancreatic function and adipose tissue expansion
- PMID: 40487622
- PMCID: PMC12142206
- DOI: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i5.101354
Neurophysiological mechanisms of electroacupuncture in regulating pancreatic function and adipose tissue expansion
Abstract
Background: Electroacupuncture (EA) has been recognized for its beneficial effects on glucolipid metabolism, potentially through the regulation of sensory nerve coordination. The expandability of peripancreatic adipose tissue (PAT) is implicated in the transition from obesity to type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). However, the specific pancreatic responses to EA require further elucidation.
Aim: To investigate the influence of EA on pancreatic glucolipid reduction level in a high-fat diet (HFD) rat model.
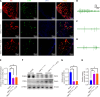
Methods: To delineate the precise pathway through which EA mediates interactions between PAT and islets, we assessed the expression levels of NGF, TRPV1, insulin, as well as other proteins in the pancreas and PAT. This approach enabled us to identify the acupoints that are most conducive to optimizing glycolipid metabolism.
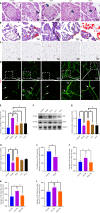
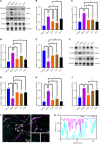
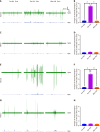
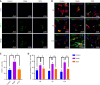
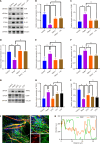
Results: The ST25, LI11 and ST37 groups attenuated HFD-induced obesity and insulin resistance (IR) to distinct degrees, with ST25 group having the greatest effect. EA at ST25 was found to modify the local regulatory influence of PAT on the pancreatic intrinsic nervous system. Specifically, EA at ST25 obviously activated the TRPV1-CGRP-islet beta cell pathway, contributing to the relief of glucolipid metabolic stress. The beneficial effects were abrogated following the chemical silencing of TRPV1 sensory afferents, confirming their indispensable role in EA-mediated regulation of islet and PAT function. Furthermore, in TRPV1 knockout mice, a reduction in PAT inflammation was observed, along with the recovery of islet beta cell function. EA at LI11 and ST37 demonstrated anti-inflammatory properties and helped ameliorate IR.
Conclusion: The PAT ecological niche influenced the progression from obesity to T2DM through various immunometabolic pathways. EA at ST25 could regulate glucolipid metabolism via the TRPV1-CGRP-islet beta cell pathway.
Keywords: Electroacupuncture; Insulin resistance; Pancreatic beta cell; Peripancreatic adipose tissue; Sensory nerve; Transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 receptor.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: There is no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this article.
Figures
References
-
- Li Y, Teng D, Shi X, Qin G, Qin Y, Quan H, Shi B, Sun H, Ba J, Chen B, Du J, He L, Lai X, Li Y, Chi H, Liao E, Liu C, Liu L, Tang X, Tong N, Wang G, Zhang JA, Wang Y, Xue Y, Yan L, Yang J, Yang L, Yao Y, Ye Z, Zhang Q, Zhang L, Zhu J, Zhu M, Ning G, Mu Y, Zhao J, Teng W, Shan Z. Prevalence of diabetes recorded in mainland China using 2018 diagnostic criteria from the American Diabetes Association: national cross sectional study. BMJ. 2020;369:m997. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yari Z, Behrouz V, Zand H, Pourvali K. New Insight into Diabetes Management: From Glycemic Index to Dietary Insulin Index. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2020;16:293–300. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

