Construction of a risk prediction model for hypertension in type 2 diabetes: Independent risk factors and nomogram
- PMID: 40487624
- PMCID: PMC12142180
- DOI: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i5.102141
Construction of a risk prediction model for hypertension in type 2 diabetes: Independent risk factors and nomogram
Abstract
Background: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a prevalent metabolic disorder increasingly linked with hypertension, posing significant health risks. The need for a predictive model tailored for T2DM patients is evident, as current tools may not fully capture the unique risks in this population. This study hypothesizes that a nomogram incorporating specific risk factors will improve hypertension risk prediction in T2DM patients.
Aim: To develop and validate a nomogram prediction model for hypertension in T2DM patients.
Methods: A retrospective observational study was conducted using data from 26850 T2DM patients from the Anhui Provincial Primary Medical and Health Information Management System (2022 to 2024). The study included patients aged 18 and above with available data on key variables. Exclusion criteria were type 1 diabetes, gestational diabetes, insufficient data, secondary hypertension, and abnormal liver and kidney function. The Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator regression and multivariate logistic regression were used to construct the nomogram, which was validated on separate datasets.
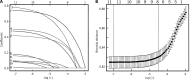
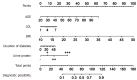
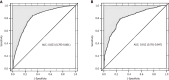
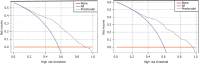
Results: The developed nomogram for T2DM patients incorporated age, low-density lipoprotein, body mass index, diabetes duration, and urine protein levels as key predictive factors. In the training dataset, the model demonstrated a high discriminative power with an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) of 0.823, indicating strong predictive accuracy. The validation dataset confirmed these findings with an AUC of 0.812. The calibration curve analysis showed excellent agreement between predicted and observed outcomes, with absolute errors of 0.017 for the training set and 0.031 for the validation set. The Hosmer-Lemeshow test yielded non-significant results for both sets (χ 2 = 7.066, P = 0.562 for training; χ 2 = 6.122, P = 0.709 for validation), suggesting good model fit.
Conclusion: The nomogram effectively predicts hypertension risk in T2DM patients, offering a valuable tool for personalized risk assessment and guiding targeted interventions. This model provides a significant advancement in the management of T2DM and hypertension comorbidity.
Keywords: Hypertension; Nomogram; Prediction model; Risk factors; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest regarding this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Development and validation of a nomogram to predict the risk of peripheral artery disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Dec 12;13:1059753. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1059753. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36578962 Free PMC article.
-
Novel model predicts diastolic cardiac dysfunction in type 2 diabetes.Ann Med. 2023 Dec;55(1):766-777. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2023.2180154. Ann Med. 2023. PMID: 36908240 Free PMC article.
-
Nomogram Prediction for the Risk of Diabetic Foot in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jul 13;13:890057. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.890057. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35909507 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Model Predicts Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients Complicated With Metabolic Syndrome Using Retrospective Dataset From First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, China.Int J Endocrinol. 2025 Apr 24;2025:9558141. doi: 10.1155/ije/9558141. eCollection 2025. Int J Endocrinol. 2025. PMID: 40313395 Free PMC article.
-
Nomogram to predict the risk of acute kidney injury in patients with diabetic ketoacidosis: an analysis of the MIMIC-III database.BMC Endocr Disord. 2021 Mar 4;21(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s12902-021-00696-8. BMC Endocr Disord. 2021. PMID: 33663489 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Predicting hypertension in type 2 diabetes mellitus: Insights from a nomogram model.World J Diabetes. 2025 Jul 15;16(7):107501. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i7.107501. World J Diabetes. 2025. PMID: 40697588 Free PMC article.
References
-
- DeFronzo RA, Ferrannini E, Groop L, Henry RR, Herman WH, Holst JJ, Hu FB, Kahn CR, Raz I, Shulman GI, Simonson DC, Testa MA, Weiss R. Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2015;1:15019. - PubMed
-
- Kamalumpundi V, Shams E, Tucker C, Cheng L, Peterson J, Thangavel S, Ofori O, Correia M. Mechanisms and pharmacotherapy of hypertension associated with type 2 diabetes. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022;206:115304. - PubMed
-
- Elhefnawy ME, Ghadzi SMS, Noor Harun S. Predictors Associated with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Complications over Time: A Literature Review. J Vasc Dis. 2022;1:13–23.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

