Antiemetic effect of acupressure wristbands for GLP-1 medication associated nausea
- PMID: 40487675
- PMCID: PMC12137197
- DOI: 10.1016/j.obpill.2025.100178
Antiemetic effect of acupressure wristbands for GLP-1 medication associated nausea
Erratum in
-
Erratum regarding missing clinical trial registration numbers in previously published articles.Obes Pillars. 2025 Jul 3;15:100193. doi: 10.1016/j.obpill.2025.100193. eCollection 2025 Sep. Obes Pillars. 2025. PMID: 40698044 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Nausea is one of the most reported side effect of GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1a). Current recommendations fall short in taming the symptoms, include antiemetic medication, behavior changes, GLP-1a dose adjustment, and often cause a disruption to treatment. Sea-Band® is a drug-free, class II FDA-cleared medical device for relief of nausea in motion sickness, morning sickness, chemotherapy and anesthesia induced nausea. The device is a set of soft, elastic, reusable acupressure wristbands (ACW) with a skin-facing plastic button worn below the wrist crease applying pressure at acupoint pericardium 6. We hypothesized that ACW was an effective tool for GLP-1a associated nausea.
Methods: This was a one-arm, open-label, non-randomized, prospective interventional study evaluating the antiemetic effect of ACW in non-pregnant adults on GLP-1as with nausea. GLP-1a were semaglutide or tirzepatide. Exclusion criteria were patients on GLP-1a without nausea, recent use of antiemetic medications, other nausea-related conditions, history of gastroparesis, and uncontrolled gastroesophageal reflux disease. Patients were shown how to properly place and use ACW at the onset of nausea and were followed weekly for 4 weeks. Follow-ups assessed frequency of nausea, ACW use frequency and duration, and change in nausea.
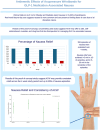
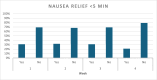
Results: 359 episodes of nausea were recorded amongst 31 adult participants over 4 weeks. Adults, mean age 55, mean BMI 34, mean HbA1c 5.9 %, reported nausea over 80 % of the time on a weekly basis. ACW were used in all recorded episodes of nausea. Medication doses were kept stable throughout the duration of this study. Nausea relief was achieved within 5 min in one third of episodes, and in over 5 min but under 20 min in the remainder of the episodes. A logistic regression model was used to evaluate the likelihood of nausea relief. A consistent rate of nausea relief over 80 % was observed during the study period, adjusting for the correlation between reduced nausea episodes and reduced episodes.
Conclusion: Although not a controlled trial, this pilot, proof of concept, pragmatic study suggests that ACW may offer a safe, self-administered, reusable, and drug-free option for managing GLP-1a associated nausea.ACW's nausea reducing effect was seen in over 80 % of episodes, and remained consistent throughout the study period. One third of participants experienced relief within 5 min of wearing ACW in the first three weeks. Given the relatively small sample size of the population, further large-scale investigations are justified. Nausea is common in day-to-day real-world use of GLP-1as, and our results suggest that using ACW may provide a first-line therapeutic intervention used ad libitum to tame a disruptive symptom, improve day-to-day well-being, and positively impact a person's treatment journey on GLP-1a.
Keywords: Acupressure; Drug-free; Glp-1 medication; Glp1; Nausea; Nausea relief.
© 2025 The Authors.
Figures



References
-
- Gregg E.W., Shaw J.E. Global health effects of overweight and obesity. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(1):80–81. - PubMed
-
- Jensen M.D., et al. 2013 AHA/ACC/TOS guideline for the management of overweight and obesity in adults: a report of the American college of cardiology/American heart association task force on practice guidelines and the obesity society. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63(25 Pt B):2985–3023. - PubMed
-
- Apovian C.M., Istfan N.W. Obesity: guidelines, best practices, new research. Endocrinol Metab Clin N Am. 2016;45(3):xvii–xviii. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

