The Nasal-Brain Drug Delivery Route: Mechanisms and Applications to Central Nervous System Diseases
- PMID: 40487748
- PMCID: PMC12141948
- DOI: 10.1002/mco2.70213
The Nasal-Brain Drug Delivery Route: Mechanisms and Applications to Central Nervous System Diseases
Abstract
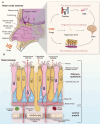
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective and protective barrier that restricts the entry of most therapeutic agents into the central nervous system (CNS), posing a significant challenge for the treatment of CNS diseases. The nose-to-brain drug delivery (NBDD) route has emerged as a promising strategy to bypass the BBB, offering direct, noninvasive, and efficient transport of drugs to the brain. This review begins with a concise overview of the BBB structure and its biofunctions, followed by an in-depth discussion of the mechanisms underlying the nose-to-brain pathway, including the olfactory and trigeminal nerve routes, and respiratory pathway. We further highlight the therapeutic research development of neurodegenerative diseases, acute neurological diseases, brain tumor, and psychiatric disorders when using NBDD drugs encompassing small-molecule drugs, proteins, peptides, nucleic acids, siRNA, and herbal compounds, in which we also introduce innovative delivery systems, including nanocarriers and novel platforms such as exosomes, which enhance drug stability, targeting efficiency, and bioavailability. In addition, we provide a comprehensive overview of recent clinical advancements in therapeutics delivered via the intranasal route for CNS diseases. Finally, we discuss the challenges and future directions of NBDD, emphasizing its potential to transform the treatment landscape for CNS disorders.
Keywords: blood–brain barrier; central nervous system diseases; drug delivery systems; intranasal administration; nose–brain drug delivery.
© 2025 The Author(s). MedComm published by Sichuan International Medical Exchange & Promotion Association (SCIMEA) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Li Yang is an employee of Sichuan Youngster Technology Co., Ltd., but has no potential relevant financial or non‐financial interests to disclose. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Goel H., Kalra V., Verma S. K., Dubey S. K., and Tiwary A. K., “Convolutions in the Rendition of Nose to Brain Therapeutics From Bench to Bedside: Feats & Fallacies,” Journal of Controlled Release 341 (2022): 782–811. - PubMed
-
- Wang C., Cui W., Yu B., et al., “Role of Succinylation Modification in central Nervous System Diseases,” Ageing Research Reviews 95 (2024): 102242. - PubMed
-
- Agrawal M., Saraf S., Saraf S., et al., “Nose‐to‐brain Drug Delivery: An Update on Clinical Challenges and Progress towards Approval of Anti‐Alzheimer Drugs,” Journal of Controlled Release 281 (2018): 139–177. - PubMed
-
- Lu J., Wang X., Wu A., et al., “Ginsenosides in central Nervous System Diseases: Pharmacological Actions, Mechanisms, and Therapeutics,” Phytotherapy Research PTR 36, no. 4 (2022): 1523–1544. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
