Identification of α2-macroglobulin as a biomarker for type 2 diabetes in human serum
- PMID: 40487757
- PMCID: PMC12140998
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1534490
Identification of α2-macroglobulin as a biomarker for type 2 diabetes in human serum
Abstract
Objectives: This study aimed to determine potential serum biomarkers of type 2 diabetes (T2DM) through proteomic data analysis and protein association assessment.
Methods: This study included 80 patients with obesity, 76 patients with newly diagnosed T2DM combined with obesity, and 73 healthy controls. Proteomics analysis was used to investigate changes in protein abundance in the serum across the three groups. Correlations were analyzed using logistic regression, Pearson's correlation, and Spearman's correlation. Group comparisons for non-normally distributed continuous or categorical variables were performed using the Mann-Whitney U test, Kruskal-Wallis test, χ2 test, or Fisher's exact probability test, as appropriate. Logistic regression analysis was employed to identify independent predictors, and correlations were evaluated using Pearson or Spearman tests based on data distribution. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was employed to determine the predictive value of the differential proteins for the diagnosis of obesity and T2DM.
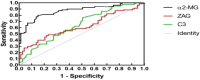
Results: In this study, two-dimensional gel electrophoresis was used to analyze three groups. Several proteins were differentially expressed, with α2-macroglobulin (α2-MG) showing significant up-regulation in the obesity and T2DM + obesity groups compared to the control group. ELISA verification showed higher α2-MG levels in the obesity (2.746±0.391 g/L) and T2DM + obesity (3.261±0.400 g/L) groups than in the control group (1.376±0.229 g/L) (P<0.05). For predicting obesity and T2DM combined with obesity, α2-MG (AUC=0.873 and 0.601 respectively) were significant predictors.
Conclusion: Serum a2-MG levels are elevated in obese individuals and those with T2DM. It shows high sensitivity and specificity for predicting obesity and T2DM, suggesting its potential as a biomarker for T2DM diagnosis. However, further large-scale studies are needed to confirm its clinical utility.
Keywords: biomarkers; mass spectrometry; obesity; proteomics; risk assessment; twodimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis; type 2 diabetes mellitus; α2-Macroglobulin.
Copyright © 2025 Wang, He, Chang and Yan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

