Research status and trends of deep learning in colorectal cancer (2011-2023): Bibliometric analysis and visualization
- PMID: 40487952
- PMCID: PMC12142239
- DOI: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i5.103667
Research status and trends of deep learning in colorectal cancer (2011-2023): Bibliometric analysis and visualization
Abstract
Background: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third-most prevalent cancer and the cancer with the second-highest mortality rate worldwide, representing a high public health burden. Deep learning (DL) offers advantages in the diagnosis, identification, localization, classification and prognosis of CRC patients. However, few bibliometric analyses of research hotspots and trends in the field have been performed.
Aim: To use bibliometric approaches to analyze and visualize the current research state and development trend of DL in CRC as well as to anticipate future research directions and hotspots.
Methods: Datasets were retrieved from the Web of Science Core Collection for the period January 2011 to December 2023. Scimago Graphica (1.0.45), VOSviewer (1.6.20) and CiteSpace (6.3.1) were used to analyze and visualize the nation, institution, journal, author, reference and keyword indicators. Origin (2022) was utilized for plotting, and Excel (2021) was used to construct the tables.
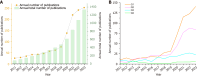
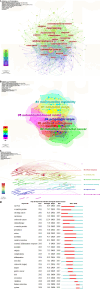
Results: A total of 1275 publications in 538 journals from 74 countries and 2267 institutions were collected. The number of annual publications has increased over time. China (371, 29.1%), the United States (265, 20.8%) and Japan (155, 12.2%) contributed significantly to the number of articles published, accounting for 62.1% of the total publications. The United States had the strongest ties to other nations. Sun Yat-sen University in China had the highest number of publications (32). The journal with the most publications was Scientific Reports (34, Q2), whereas Gastrointestinal Endoscopy had the most co-citations (1053, Q1). Kather JN, was the author with the most articles (12) and co-citations (287). The most frequently cited reference was Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. Keywords were divided into six clusters, with "colorectal cancer" (12.34) having the highest outbreak intensity.
Conclusion: This study highlights the current status and most active directions of the use of DL in CRC. This approach has important applications in the identification, diagnosis, localization, classification and prognosis of the disease and will remain a central focus in the future.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Bibliometric analysis; Colorectal cancer; Deep learning; Visualization.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Research Trends in the Application of Artificial Intelligence in Oncology: A Bibliometric and Network Visualization Study.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022 Aug 31;27(9):254. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2709254. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022. PMID: 36224012
-
Application of artificial intelligence in Alzheimer's disease: a bibliometric analysis.Front Neurosci. 2025 Feb 14;19:1511350. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1511350. eCollection 2025. Front Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40027465 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research trends on the relationship between gut microbiota and colorectal cancer: A bibliometric analysis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Jan 9;12:1027448. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1027448. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36699721 Free PMC article.
-
The global research of artificial intelligence in lung cancer: a 20-year bibliometric analysis.Front Oncol. 2024 Feb 2;14:1346010. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1346010. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38371616 Free PMC article.
-
Research hotspots and frontiers of machine learning in renal medicine: a bibliometric and visual analysis from 2013 to 2024.Int Urol Nephrol. 2025 Mar;57(3):907-928. doi: 10.1007/s11255-024-04259-3. Epub 2024 Oct 30. Int Urol Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39472403 Review.
References
-
- Zhang X, Yang L, Liu S, Cao LL, Wang N, Li HC, Ji JF. [Interpretation on the report of global cancer statistics 2022] Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2024;46:710–721. - PubMed
-
- Acs B, Rantalainen M, Hartman J. Artificial intelligence as the next step towards precision pathology. J Intern Med. 2020;288:62–81. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

