Hepatitis B core-related antigen as a predictive biomarker for recurrence in primary hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 40487961
- PMCID: PMC12142257
- DOI: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i5.105148
Hepatitis B core-related antigen as a predictive biomarker for recurrence in primary hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common malignancies, with high recurrence rates after treatment. Identifying reliable biomarkers for predicting recurrence is essential for improving patient outcomes. Hepatitis B core-related antigen (HBcrAg) has shown potential as a predictive marker for HCC recurrence.
Aim: To evaluate the association between HBcrAg levels and the risk of HCC recurrence.
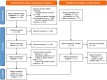
Methods: A systematic review was conducted following PRISMA guidelines. PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science, and the Cochrane Library were searched without restrictions on date or language. Observational studies reporting hazard ratios (HRs) for HBcrAg as a predictor of HCC recurrence were included. Data extraction and quality assessment were performed independently by two reviewers. Statistical analyses used a random-effects model to account for heterogeneity (I² ≥ 50%), and sensitivity analysis was performed to ensure the robustness of the results.
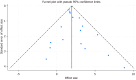
Results: A total of 1339 articles were initially identified, and 17 studies were included in the final meta-analysis after screening. The pooled analysis showed a significant association between elevated HBcrAg levels and HCC recurrence (HR = 4.42, 95% confidence interval: 3.43-5.41) with substantial heterogeneity (I² = 92.6%). Subgroup analysis revealed higher pooled HRs in studies with ≥ 500 participants (HR = 4.18) and HBcrAg cut-offs ≥ 4.0 LogU/mL (HR = 5.29). Studies with ≥ 10 years of follow-up showed a lower HR (2.89) compared to those with < 10 years (3.27). Patients treated with nucleos(t)ide analogs had a pooled HR of 1.98, while those without nucleos(t)ide analog had a higher HR of 3.87. Sensitivity analysis confirmed the robustness of the results, with no significant publication bias detected.
Conclusion: This meta-analysis provides strong evidence that elevated HBcrAg levels are associated with an increased risk of HCC recurrence. HBcrAg may serve as a valuable biomarker for predicting recurrence, aiding personalized management and surveillance strategies for HCC patients.
Keywords: Hepatitis B core-related antigen; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Meta-analysis; Predictive biomarker; Recurrence.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Role of hepatitis B core-related antigen in predicting the occurrence and recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic hepatitis B: A systemic review and meta-analysis.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Aug;39(8):1464-1475. doi: 10.1111/jgh.16558. Epub 2024 Apr 30. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38686439
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
HBcrAg predicts hepatocellular carcinoma development: An analysis using time-dependent receiver operating characteristics.J Hepatol. 2016 Jul;65(1):48-56. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.03.013. Epub 2016 Mar 29. J Hepatol. 2016. PMID: 27034253
-
Impact of hepatitis B core-related antigen on the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients treated with nucleos(t)ide analogues.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2019 Feb;49(4):457-471. doi: 10.1111/apt.15108. Epub 2019 Jan 20. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2019. PMID: 30663078
-
Three heads are better than two: Hepatitis B core-related antigen as a new predictor of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma.Clin Mol Hepatol. 2021 Oct;27(4):524-534. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2021.0012. Epub 2021 Feb 23. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33618507 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chen S, Huang C, Liao G, Sun H, Xie Y, Liao C, Wang J, He M, Hu H, Dai Z, Ren X, Zeng X, Lin Z, Zhang GP, Xie W, Shen S, Li S, Peng S, Kuang DM, Zhao Q, Duda DG, Kuang M. Distinct single-cell immune ecosystems distinguish true and de novo HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma recurrences. Gut. 2023;72:1196–1210. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

