Anti- Trypanosoma cruzi Effect of Fatty Acids from Porcelia macrocarpa Is Related to Interactions of Cell Membranes at Different Microdomains as Assessed Using Langmuir Monolayers
- PMID: 40488021
- PMCID: PMC12138661
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.5c01382
Anti- Trypanosoma cruzi Effect of Fatty Acids from Porcelia macrocarpa Is Related to Interactions of Cell Membranes at Different Microdomains as Assessed Using Langmuir Monolayers
Abstract
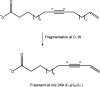
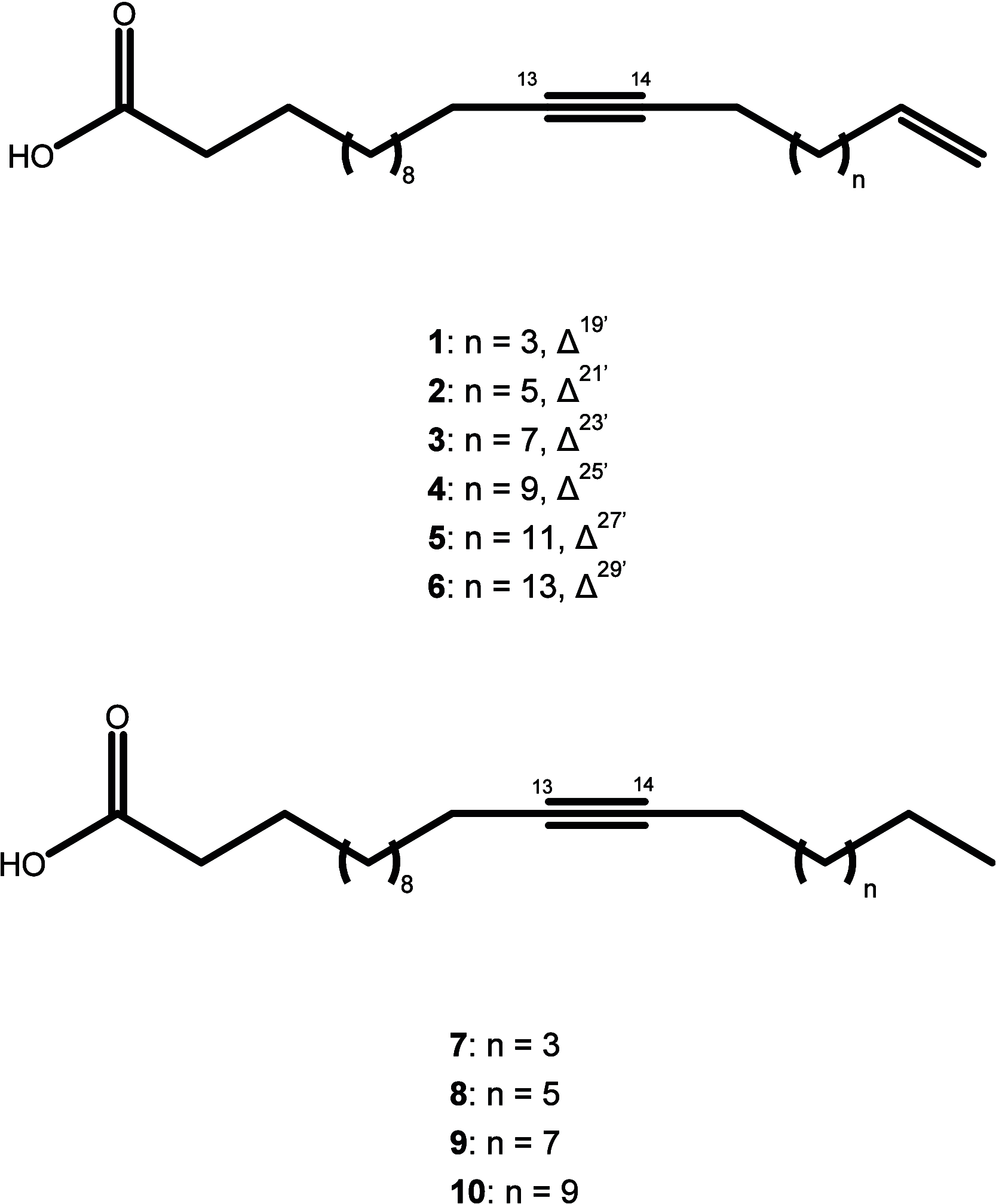
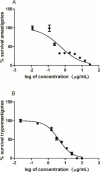
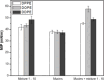
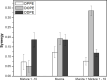
Chagas disease, a parasitic disease caused by the protozoan Trypanosoma cruzi, is an important health problem affecting more than 8 million people worldwide. The only available treatments, benznidazole and nifurtimox, display high toxicity and reduced efficacy in the chronic phase of the disease. To find new natural products with anti-T. cruzi activity, the CH2Cl2 extract of Porcelia macrocarpa R. E. Fries (Annonaceae) seeds was subjected to bioactivity-guided fractionation. Through several chromatographic steps, one group consisting of a mixture of 10 chemically related fatty acids (1-10) was obtained. This group showed activity against trypomastigote forms with an EC50 of 4.0 μg/mL, similar to the standard drug benznidazole (EC50 = 3.9 μg/mL). It also showed activity against the intracellular amastigotes, with an EC50 of 0.5 μg/mL, close to the efficacy of benznidazole (EC50 = 0.9 μg/mL). In addition, the mixture of 1-10 showed no toxicity against murine fibroblasts (CC50 > 200 μg/mL), resulting in SI > 49 and >416 in trypomastigotes and amastigotes, respectively. The interaction of the mixture with the protozoan membrane models was also assessed with Langmuir monolayers composed of three phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) lipids with different degrees of acyl chain unsaturation and in the presence of mucins. Compounds 1-10 favorably interact with all tested lipids, with maximum insertion pressure (MIP) values above 40 mN/m and positive synergy values, suggesting penetration through the mucins. Furthermore, the mixture has a higher affinity for monounsaturated lipids bound to mucins, with an MIP value of 57.59 ± 2.59 mN/m. Based on these results, the effect of compounds 1-10 against T. cruzi can be related to interactions with the parasite cell membranes.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enyne acetogenins from Porcelia macrocarpa displayed anti-Trypanosoma cruzi activity and cause a reduction in the intracellular calcium level.Sci Rep. 2023 Jun 24;13(1):10254. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-37520-3. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37355735 Free PMC article.
-
Homologous acetylenic acetogenins from Porcelia macrocarpa R.E. (Fries) displayed potent activity against amastigotes from Trypanosoma cruzi.Phytochemistry. 2025 Mar;231:114360. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2024.114360. Epub 2024 Dec 12. Phytochemistry. 2025. PMID: 39672219
-
Acetylenic fatty acids from Porcelia macrocarpa (Annonaceae) against trypomastigotes of Trypanosoma cruzi: Effect of octadec-9-ynoic acid in plasma membrane electric potential.Bioorg Chem. 2018 Aug;78:307-311. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2018.03.025. Epub 2018 Mar 30. Bioorg Chem. 2018. PMID: 29625270
-
Experimental models in Chagas disease: a review of the methodologies applied for screening compounds against Trypanosoma cruzi.Parasitol Res. 2018 Nov;117(11):3367-3380. doi: 10.1007/s00436-018-6084-3. Epub 2018 Sep 19. Parasitol Res. 2018. PMID: 30232605 Review.
-
The Potential of Secondary Metabolites from Plants as Drugs or Leads against Trypanosoma cruzi-An Update from 2012 to 2021.Curr Top Med Chem. 2023;23(3):159-213. doi: 10.2174/1568026623666221212111514. Curr Top Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36515019 Review.
References
-
- Porrás A. I., Yadon Z. E., Altcheh J., Britto C., Chaves G. C., Flevaud L., Martins-Filho O. A., Ribeiro I., Schijman A. G., Shikanai-Yasuda M. A., Sosa-Estani S., Stobbaerts E., Zicker F.. Target product profile (TPP) for Chagas disease point-of-care diagnosis and assessment of response to treatment. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015;9:e0003697. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003697. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Oliveira E. A., Brito I. A., Lima M. L., Romanelli M., Moreira-Filho J. T., Neves B. J., Andrade C. H., Sartorelli P., Tempone A. G., Costa-Silva T. A., Lago J. H. G.. Antitrypanosomal activity of acetogenins isolated from the seeds of Porcelia macrocarpa is associated with alterations in both plasma membrane electric potential and mitochondrial membrane potential. J. Nat. Prod. 2019;82:1177–1182. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.8b00890. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
