Network Pharmacology Combined with Proteomics Reveals That 3‑Acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic Acid Inhibits the Progression of Prostate Cancer by Regulating the IL-17 Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 40488086
- PMCID: PMC12138829
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.5c01683
Network Pharmacology Combined with Proteomics Reveals That 3‑Acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic Acid Inhibits the Progression of Prostate Cancer by Regulating the IL-17 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
Background: 3-acetyl-11-keto-beta-boswellic acid (AKBA) is a monomer extracted from the traditional Chinese herbs of Boswellia that has antitumor effects. However, the therapeutic effects and mechanisms of AKBA in prostate cancer (PCa) are unclear.
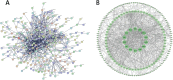
Objective: To predict the target of AKBA treatment of PCa using network pharmacology methods and validate the predicted targets through CCK-8, flow cytometry, cell scratch test, Transwell chamber assay, and proteomics.
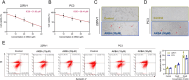
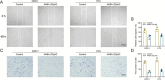
Methods: The protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was established. Further analysis was performed by gene ontology (GO) and the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes for biological functionality and pathway enrichment. CCK-8 assay, flow cytometry, wound healing assay, and Transwell chamber assay were used to detect cell proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, and metastasis, respectively. Transcriptomics was used to detect the effects of AKBA on protein levels in PCa cells.
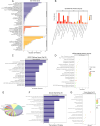
Results: 120 potential targets for the AKBA treatment of PCa were obtained. GO enrichment analysis revealed that the biological processes of AKBA treatment of PCa include the steroid metabolic process, drug response, and fatty acid metabolic process. The results of KEGG enrichment revealed that the IL-17 signaling pathway is the key pathway for the AKBA treatment of PCa. In addition, experimental results demonstrate that AKBA inhibits the proliferation of PCa cells, induces cell apoptosis, and suppresses cell invasion and metastasis. Proteomics identified 119 differentially expressed proteins, which were primarily enriched in pathways closely related to the phogosome, pathways in cancer, IL-17 signaling pathway, spliceosome, PPAR signaling pathway, and HIF-1 signaling pathway.
Conclusion: Through the methodologies of network pharmacology and transcriptomics, AKBA may exert its therapeutic effects on PCa by modulating the expression of the IL-17 signaling pathway.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid suppresses docetaxel-resistant prostate cancer cells in vitro and in vivo by blocking Akt and Stat3 signaling, thus suppressing chemoresistant stem cell-like properties.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019 May;40(5):689-698. doi: 10.1038/s41401-018-0157-9. Epub 2018 Aug 31. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019. PMID: 30171201 Free PMC article.
-
Acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of gastric cancer cells through the phosphatase and tensin homolog /Akt/ cyclooxygenase-2 signaling pathway.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 Oct 14;26(38):5822-5835. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i38.5822. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 33132637 Free PMC article.
-
Network pharmacology and experimental validation to explore the role and potential mechanism of Liuwei Dihuang Decoction in prostate cancer.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024 Jul 26;24(1):284. doi: 10.1186/s12906-024-04572-5. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024. PMID: 39061044 Free PMC article.
-
3-O-acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid exerts anti-tumor effects in glioblastoma by arresting cell cycle at G2/M phase.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Jul 3;37(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0805-4. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29970196 Free PMC article.
-
The Biological Activity of 3-O-Acetyl-11-keto-β-Boswellic Acid in Nervous System Diseases.Neuromolecular Med. 2022 Dec;24(4):374-384. doi: 10.1007/s12017-022-08707-0. Epub 2022 Mar 18. Neuromolecular Med. 2022. PMID: 35303275 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pan X., Chen K., Gao W., Xu M., Meng F., Wu M., Wang Z. Q., Li Y. Q., Xu W., Zhang M.. et al. Circular RNA circBNC2 inhibits tumorigenesis by modulating ferroptosis and acts as a nanotherapeutic target in prostate cancer. Mol. Cancer. 2025;24(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s12943-025-02234-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li W., Liu H., Zheng J.. et al. Kaempferol modulates α2M secretion in bone marrow-derived macrophages by downregulating GR/PER1-mediated lipid metabolism to attenuate the emotional stress-aggravated metastasis of prostate cancer. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2025;339:119162. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.119162. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
