Challenges and Opportunities: Interplay between Infectious Disease and Antimicrobial Resistance in Medical Device Surface Applications
- PMID: 40488087
- PMCID: PMC12138651
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.5c01011
Challenges and Opportunities: Interplay between Infectious Disease and Antimicrobial Resistance in Medical Device Surface Applications
Abstract
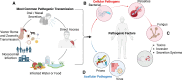
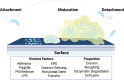
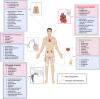
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a growing silent pandemic driven by multidrug-resistant infections, particularly those associated with medical devices such as dental implants, heart valves, and urinary catheters. This review addresses the urgent need for alternative antimicrobial strategies by exploring the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in the discovery of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) and the rational design of bioactive surfaces. We describe how AI-based models accelerate the identification and optimization of peptide candidates with potent antibiofilm activity. Moreover, we examine recent advancements in surface engineering, such as biomimetic coatings, quorum sensing inhibitors, and enzyme-based strategies, that disrupt bacterial colonization and biofilm formation. The novelty of this work lies in its unified perspective that bridges computational prediction, materials science, and microbial pathogenesis to inform the next generation of antimicrobial surfaces. By highlighting innovative AI-assisted approaches and emerging hybrid strategies, this review underscores their potential to mitigate device-associated infections and address the broader challenge of AMR in healthcare settings.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Figures




Similar articles
-
AI-Driven Antimicrobial Peptide Discovery: Mining and Generation.Acc Chem Res. 2025 Jun 17;58(12):1831-1846. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00594. Epub 2025 Jun 3. Acc Chem Res. 2025. PMID: 40459283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selected honey as a multifaceted antimicrobial agent: review of compounds, mechanisms, and research challenges.Future Microbiol. 2025 May-Jun;20(7-9):589-610. doi: 10.1080/17460913.2025.2498233. Epub 2025 Apr 28. Future Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40293032 Review.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Targeting Ocular Biofilms with Plant-Derived Antimicrobials in the Era of Antibiotic Resistance.Molecules. 2025 Jul 5;30(13):2863. doi: 10.3390/molecules30132863. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40649377 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnaiz-Villena A., Juarez I., Vaquero-Yuste C., Lledo T., Martin-Villa J. M., Suarez-Trujillo F.. Complex Interactions between the Human Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) and Microbiota: Their Roles in Disease Pathogenesis and Immune System Regulation. Biomedicines. 2024;12(8):1928. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12081928. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Charitos I. A., Scacco S., Cotoia A., Castellaneta F., Castellana G., Pasqualotto F., Venneri M., Ferrulli A., Aliani M., Santacroce L.. et al. Intestinal Microbiota Dysbiosis Role and Bacterial Translocation as a Factor for Septic Risk. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025;26(5):2028. doi: 10.3390/ijms26052028. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
