Effect of Introducing Leucine Residues into 2‑Aminoisobutyric Acid-Based Amphiphilic Helical Peptides on Intermolecular Interactions and Peptide Self-Assembly
- PMID: 40488101
- PMCID: PMC12138716
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.5c02490
Effect of Introducing Leucine Residues into 2‑Aminoisobutyric Acid-Based Amphiphilic Helical Peptides on Intermolecular Interactions and Peptide Self-Assembly
Abstract
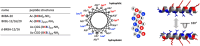
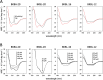
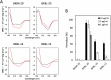
In recent years, self-assembling de novo-designed peptides have attracted increasing attention as materials for constructing submicrometer-scale structures. We have previously conducted structure-activity relationship studies on the BXBA-20 series of 20-residue amphiphilic peptides containing 2-aminoisobutyric acid (Aib) [Higashimoto, Y. et al. (1999) J. Biochem. 125, 705-712; Hara, T. et al. (2001) J. Biochem. 130, 749-755; Taira, J. et al. (2010) J. Pept. Sci. 16, 607-612]. These peptides share the common sequence Ac-(Aib-Xxx-Aib-Ala)5-NH2, where the introduction of a hydrophilic amino acid at the Xxx position results in the formation of a hydrophilic face on one side of the helix. Among them, some peptides exhibited weak intermolecular association and interactions with lipid membranes, though none demonstrated the ability to form submicrometer-scale structures through self-assembly. In this study, we present BKBL-20, a new member of this peptide series incorporating leucine on the hydrophobic face and lysine on the hydrophilic face. Circular dichroism spectroscopy indicated strong association in buffer, while hemolysis assays revealed significant membrane disruption. Transmission electron microscopy further confirmed the formation of ordered fibrous or array-like structures. These findings suggest that BKBL-20 successfully combines self-assembly and membrane-disruptive functions.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
