Oxidative stress in periodontitis and the application of antioxidants in treatment: a narrative review
- PMID: 40488141
- PMCID: PMC12141859
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1485367
Oxidative stress in periodontitis and the application of antioxidants in treatment: a narrative review
Abstract
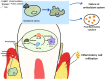
Periodontitis has turned into a general oral disease defined by chronic inflammation of the gums and helping tissues of the teeth. It dramatically influences both oral and systemic health and is a main trigger of tooth loss. Periodontitis is tightly linked to oxidative stress, and evidence reveals the utilization of certain antioxidants in related treatments. Our review delves into literature in periodontitis, centering on the latest therapeutic strategies and mechanistic evidences. This review starts by depicting the epidemiological features and pathogenic mechanisms of periodontitis, highlighting the vital mechanism of microbial community modefications, host immune responses, and genetic factors in disease development. Existing treatment approaches for periodontitis involve mechanical cleaning, antibiotic therapy, surgical interventions, and pharmacological treatments, with a comprehensive exploration on the strengths and limitations of each strategy and their related clinical utilizations. Besides, this review investigates emerging therapies, like anti-inflammatory treatments, immune modulation therapies, and biotechnological utilization in the control of periodontitis. It particularly stresses the protective effects of antioxidants and their mechanistic researches in periodontitis, highlighting their potential in slowing inflammatory responses and boosting tissue repair. Ultimately, our review intends to the concept of individual therapy and investigates future directions, comprising the utilization of precision medicine in periodontitis control and the individual design of treatment utilization.
Keywords: antioxidants; inflammation; oxidative stress; periodontitis; tissue repair.
Copyright © 2025 Liu and Guo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Periodontitis: etiology, conventional treatments, and emerging bacteriophage and predatory bacteria therapies.Front Microbiol. 2024 Sep 26;15:1469414. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1469414. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39391608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Host modulation therapy using anti-inflammatory and antioxidant agents in periodontitis: A review to a clinical translation.Arch Oral Biol. 2019 Sep;105:72-80. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2019.07.002. Epub 2019 Jul 3. Arch Oral Biol. 2019. PMID: 31288144 Review.
-
Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease of oxidative stress: We should treat it that way.Periodontol 2000. 2020 Oct;84(1):45-68. doi: 10.1111/prd.12342. Periodontol 2000. 2020. PMID: 32844417 Review.
-
Periodontal Disease as a Risk Factor for Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review.JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2012;10(42 Suppl):1-12. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2012-288. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 27820156
-
Targeting Nrf2 with Probiotics and Postbiotics in the Treatment of Periodontitis.Biomolecules. 2022 May 22;12(5):729. doi: 10.3390/biom12050729. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35625655 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Periodontal Health and Total Antioxidant Capacity for Jordanian Smokers at Dental Teaching Clinic.Int J Dent. 2025 Jul 21;2025:3075190. doi: 10.1155/ijod/3075190. eCollection 2025. Int J Dent. 2025. PMID: 40726823 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bagatini M., Assmann C., Blumenberg M. (2020). Glutathione system and oxidative stress in health and diseaseM BoD–Books on Demand.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

