An anatomically enhanced and clinically validated framework for lung abnormality classification using deep features and KL divergence
- PMID: 40488166
- PMCID: PMC12141059
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mex.2025.103348
An anatomically enhanced and clinically validated framework for lung abnormality classification using deep features and KL divergence
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to: "An Anatomically Enhanced and Clinically Validated Framework for Lung Abnormality Classification Using Deep Features and KL Divergence" [MethodsX, Volume 14 (June 2025), Article Number: 103348].MethodsX. 2025 Jul 4;15:103489. doi: 10.1016/j.mex.2025.103489. eCollection 2025 Dec. MethodsX. 2025. PMID: 40687350 Free PMC article.
Abstract
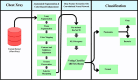
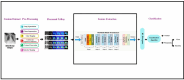
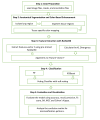
Detecting lung abnormalities via chest X-rays is challenging due to understated tissue variations often ignored by traditional methods. Augmentation techniques like rotation or flipping risk distorting critical anatomical features, actually leading to misdiagnosis. This paper proposes a novel two-stage ASCE (Anatomical Segmentation and Color-Based Enhancement) framework for precise and efficient classification of lung abnormalities while preserving anatomical integrity. Stage 1 classifies Normal vs. Pneumonia with 95 % accuracy, an AUC of 0.98, and an F1-score of 0.92. Stage 2 distinguishes Pneumonia into Viral and Bacterial subtypes with 100 % accuracy and F1-score. This approach integrates segmentation and tissue-specific color enhancements with Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence, quantifying deviations from healthy lung regions for improved classification. The lightweight pipeline ensures computational efficiency (∼0.06s/image) and clinical interpretability by preserving diagnostic features, enhancing visibility, and enabling quantitative analysis.1.Preserving Anatomical Structures: The methodology ensures that diagnostic features are preserved and highlighted with Anatomy-Preserved Segmentation2.Enhancing Diagnostic Visibility: The system employs targeted colour-based enhancement that improves the visibility of potential abnormalities3.Quantitative Analysis with Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence: The model enhances precise identification of abnormal tissue by comparing the probability distributions of healthy lungs and abnormal areas.
Keywords: Anatomical Segmentation and Color-Based Enhancement; Anatomical segmentation; Chest X-rays; Color based enhancement; Deep learning; KL divergence; Lung Abnormality; Pneumonia Detection.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Hassanpour H., Samadiani N., Mahdi Salehi S.M. Using morphological transforms to enhance the contrast of medical images. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nuclear Med. 2015;46(2):481–489. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrnm.2015.01.004. -06. - DOI
-
- Siracusano G., La Corte A., Gaeta M., Cicero G., Chiappini M., Finocchio G. Pipeline for advanced contrast enhancement (PACE) of chest X-ray in evaluating COVID-19 patients by combining bidimensional empirical mode decomposition and contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization (CLAHE) Sustainability. 2020;12(20):8573. doi: 10.3390/su12208573. -10-16. - DOI
-
- Singh A., Bhateja V., Rathore A.S., Shukla A. In: Evolution in Signal Processing and Telecommunication Networks. Chowdary P.S.R., Anguera J., Satapathy S.C., Bhateja V., editors. Vol. 839. Springer; Singapore: 2022. Contrast enhancement of CT-scan images of lungs using morphological filters; pp. 241–247.https://link.springer.com/10.1007/978-981-16-8554-5_24 (Evolution in Signal Processing and Telecommunication Networks). Series Title: Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering. Available from: - DOI
-
- Rao K., Bansal M., Kaur G. An effective CT medical image enhancement system based on DT-CWT and adaptable morphology. Circuits. Syst. Signal. Process. 2023;42(2):1034–1062. doi: 10.1007/s00034-022-02163-8. - 02. - DOI
-
- Pagadala P.K., Pinapatruni S.L., Kumar C.R., Katakam S., Peri L.S.K., Reddy D.A. Enhancing lung cancer detection from lung CT scan using image processing and deep neural networks. Revue d’Intelligence Artificielle. 2023;37(6) doi: 10.18280/ria.370624. -12-27. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

