Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo a systematic review of the effects of comorbidities
- PMID: 40488199
- PMCID: PMC12141001
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1595693
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo a systematic review of the effects of comorbidities
Abstract
Background: The prevalence of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) increases with age, as does the occurrence of other chronic health conditions. Although treatment with canalith-repositioning procedures (CRPs) is relatively successful, efficacy on the first attempt varies. Several studies have examined the influence of risk factors on BPPV occurrence and the efficacy of initial CRPs. However, findings are controversial. The objective of this study is to identify comorbidities associated with BPPV occurrence and explore their influence on the success of initial CRPs.
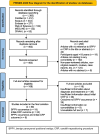
Methods: The electronic databases PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, Embase, MEDLINE and CINAHL were searched to identify eligible English original studies published from January 2019 to June 2024. All search results were reviewed based on our inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Results: Of the 463 studies identified, 50 studies that satisfied the inclusion criteria were analysed. Eighteen studies focused on BPPV occurrence, 24 on the initial-CRP outcome and eight on both BPPV occurrence and the initial-CRP outcome. Twenty-five risk factors and comorbidities were identified to be associated with BPPV occurrence, and 15 were noted to impact the efficacy of the initial CRP. The most common reported risk factor for BPPV occurrence was head trauma (16 studies) and showed the poorest success rate after one CRP requiring a maximum of 18 manoeuvres to reach complete resolution (9 studies). Other factors included cardiovascular and endocrine comorbidities, neurological/neurotological comorbidities, musculoskeletal comorbidities, anxiety, obsessive-compulsive disorder, body mass index, serum vitamin D level and idiopathic BPPV.
Conclusion: This systematic review assess the strength of evidence of risk factors influencing the development of BPPV and outcome of the initial CRP. Hypertension, hypotension, anaemia, ischaemic heart disease, hyperlipidaemia, stroke, diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, migraine, vestibular disorders, peripheral neuropathy, osteoporosis, cervical spondylosis, head trauma and low vitamin D were associated with BPPV incidence. Low levels of vitamin D, head trauma, migraine, inner ear diseases including Ménière's disease, hypertension, high cholesterol, diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, hyperlipidaemia, osteoporosis, and reduced cervical mobility are all associated with failed first canal repositioning manoeuvre. There is an identified need to explore risk factors across different BPPV subtypes and their impact on the efficacy of various treatment manoeuvres.
Keywords: BPPV; CRP; comorbidity; efficacy; occurrence; risk factors.
Copyright © 2025 Alolayet and Murdin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ciodaro F, Mannella VK, Nicita RA, Cammaroto G, Bruno R, Galletti B, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of the Galletti–Contrino manoeuvre for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo of vertical semicircular canals in overweight subjects. Eur Arch Otorrinolaringol. (2018) 275:2449–55. doi: 10.1007/s00405-018-5086-1 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous