The Protective Effects of Chrysin on Acrylamide-Induced Hepatotoxicity: Insights Into Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, Apoptosis, Autophagy, and Histological Evaluation in Rats
- PMID: 40488268
- PMCID: PMC12147197
- DOI: 10.1002/jbt.70334
The Protective Effects of Chrysin on Acrylamide-Induced Hepatotoxicity: Insights Into Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, Apoptosis, Autophagy, and Histological Evaluation in Rats
Abstract
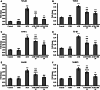
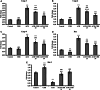
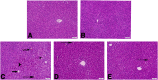
Acrylamide (ACR) is a toxic chemical with a high carcinogenic risk that is released as a result of heating or processing foods at high temperatures. Chrysin (CHR) is a flavonoid that is naturally found in foods such as honey and passionflower and stands out with its antioxidant, anticancer, and anti-inflammatory properties. This study aims to determine the protective effects of CHR in ACR-induced hepatotoxicity. ACR was administered orally at a dose of 38.27 mg/kg; CHR (25 or 50 mg/kg) was administered orally for ten days. Biochemical and molecular methods were used to investigate oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptotic markers in liver tissue. Additionally, histological methods were used to determine the liver tissue's structural and functional characteristics and autophagy. CHR treatment alleviated ACR-induced oxidative stress by increasing antioxidants (SOD, CAT, GPx, GSH) and reducing increased oxidant MDA. CHR reduced inflammatory activity by inactivating NF-κB and pro-inflammatory cytokines. ACR-induced increases in apoptotic Casp-3, Casp-6, Casp-9, and Bax were reduced by CHR, while the decreased level of antiapoptotic Bcl-2 was increased. It was also determined immunohistochemically that CHR inhibited autophagic Beclin-1 activity. CHR was effective in reducing ACR-induced hepatotoxicity damage and may be an effective treatment option.
Keywords: acrylamide; apoptosis; autophagy; chrysin; hepatotoxicity; inflammation.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

