Pre-admission beta-blocker therapy and outcomes in cardiogenic shock: Insights from the Altshock-2 Registry
- PMID: 40488449
- PMCID: PMC12287813
- DOI: 10.1002/ehf2.15322
Pre-admission beta-blocker therapy and outcomes in cardiogenic shock: Insights from the Altshock-2 Registry
Abstract
Aims: We aimed to assess the impact of pre-admission beta-blocker (BB) therapy on the clinical characteristics, in-hospital treatment and outcomes of patients with cardiogenic shock (CS).
Methods: All patients enrolled in the multicentre prospective Altshock-2 registry since March 2020 with available data on pre-admission BB therapy were included. Clinical characteristics, in-hospital management, haemodynamic parameters and clinical outcomes were compared in patients with versus without BB therapy. The primary endpoint was in-hospital mortality.
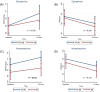
Results: A total of 668 patients were included [median age 66 (56-74) years, male sex 76.5%]: 299 patients (44.8%) with and 369 patients (55.2%) without previous BB therapy. Patients receiving pre-admission BB therapy had more frequently heart failure-related CS (43.8% vs. 17.9%) and less frequently cardiac arrest at presentation (20.1% vs. 27.8%, P = 0.027). Levosimendan was used less frequently and dobutamine was used more frequently in patients with baseline BB therapy (P = 0.033 and P = 0.043, respectively). Differences in the early haemodynamic response to vasoactive drugs were observed between patients with and without previous BB therapy, with a significant impact of baseline BB on mean arterial pressure (MAP) response during norepinephrine infusion (P = 0.012) and with dobutamine having a reduced response in MAP and heart rate in patients receiving BBs before admission (P = 0.023 and P = 0.001, respectively). In-hospital mortality was not significantly different between the BB and no-BB groups (40% vs. 33.7%; adjusted odds ratio 1.32, 95% confidence interval 0.84-2.07, P = 0.224). Similarly, baseline BB therapy was not independently associated with 48 h mortality (12.7% vs. 14.6%; adjusted odds ratio 1.09, 95% confidence interval 0.64-1.87, P = 0.749). The lack of association between baseline BB therapy and mortality was also confirmed at inverse probability of treatment weighting-adjusted analysis.
Conclusions: In a real-world, contemporary cohort of patients with CS, previous BB therapy influenced the haemodynamic response to vasoactive drugs, but it was not associated with in-hospital mortality.
Keywords: Cardiogenic shock; beta‐blockers; inotropes; mortality; vasopressors.
© 2025 The Author(s). ESC Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Pagnesi has received personal fees from Abbott Vascular, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Roche Diagnostics and Vifor Pharma. Dr. Sacco and Dr. Morici received institutional grant support from Getinge Global US; Dr. Sacco received speaker honoraria from AstraZeneca and Menarini. Dr. Marini received consulting/speaker honoraria from AstraZeneca, Orion and Abiomed. Dr. Pappalardo is a consultant for Abiomed. Dr. Metra has received consulting honoraria as a member of trial committees or advisory boards for Abbott Vascular, Actelion, Amgen, Bayer, Edwards Therapeutics, Servier, Vifor Pharma and Windtree Therapeutics. All other authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Inotropic agents and vasodilator strategies for the treatment of cardiogenic shock or low cardiac output syndrome.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 29;1(1):CD009669. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009669.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Nov 5;11:CD009669. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009669.pub4. PMID: 29376560 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
DanGer Shock-like profile predicts the outcome in ST-elevation myocardial infarction-related cardiogenic shock.ESC Heart Fail. 2025 Aug;12(4):2759-2768. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.15269. Epub 2025 Mar 19. ESC Heart Fail. 2025. PMID: 40108949 Free PMC article.
-
Inotropes and mortality in patients with cardiogenic shock: an instrumental variable analysis from the SWEDEHEART registry.Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother. 2025 Feb 8;11(1):57-65. doi: 10.1093/ehjcvp/pvae078. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother. 2025. PMID: 39415431 Free PMC article.
-
Lactate Values and Mortality in Patients With Cardiogenic Shock: Insights From the Altshock-2 Registry.Crit Care Med. 2025 Aug 1;53(8):e1620-e1629. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000006738. Epub 2025 Jun 12. Crit Care Med. 2025. PMID: 40504883
-
Inotropes for the prevention of low cardiac output syndrome and mortality for paediatric patients undergoing surgery for congenital heart disease: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 26;11(11):CD013707. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013707.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39588800 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chioncel O, Parissis J, Mebazaa A, Thiele H, Desch S, Bauersachs J, et al. Epidemiology, pathophysiology and contemporary management of cardiogenic shock—a position statement from the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur J Heart Fail 2020;22:1315‐1341. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.1922 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Metra M, Nodari S, D'Aloia A, Muneretto C, Robertson AD, Bristow MR, et al. Beta‐blocker therapy influences the hemodynamic response to inotropic agents in patients with heart failure: a randomized comparison of dobutamine and enoximone before and after chronic treatment with metoprolol or carvedilol. J Am Coll Cardiol 2002;40:1248‐1258. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(02)02134-4 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

