The impact of physical exercise on university students' life satisfaction: The chain mediation effects of general self-efficacy and health literacy
- PMID: 40489508
- PMCID: PMC12148183
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0325835
The impact of physical exercise on university students' life satisfaction: The chain mediation effects of general self-efficacy and health literacy
Abstract
Objective: This study aims to explore the impact of physical exercise on university students' life satisfaction and analyses the chain mediation effect of general self-efficacy and health literacy, providing empirical reference and theoretical foundation for the comprehensive enhancement and optimization of students' mental health.
Method: Based on data from the "China University Student Physical Activity and Health Tracking Survey" (CPAHLS-CS) 2024, the measurement scales used included the Physical Activity Rating Scale (PARS-3), the Satisfaction with Life Scale (SWLS), the General Self-Efficacy Scale (GSES), and the 9-item Short Form Health Literacy Scale (HLS-SF9). A total of 4575 valid samples were analyzed.
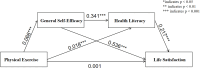
Results: A significant positive correlation was found between physical exercise and life satisfaction (r = 0.137, P < 0.01). The total effect of physical exercise on university students' life satisfaction was significant, with an effect value of 0.045 (95%CI = [0.035, 0.054]). The chain mediation effect of general self-efficacy and health literacy in the relationship between physical exercise and life satisfaction was significant, with an effect value of 0.005 (95%CI = [0.004, 0.006]), accounting for 11.4% of the total effect. The direct effect of physical exercise on life satisfaction had a standardized regression coefficient of 0.001, which was not significant.
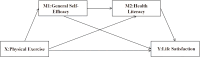
Conclusion: University students' life satisfaction is closely related to physical exercise, general self-efficacy, and health literacy. General self-efficacy and health literacy play a full mediating role in the effect of physical exercise on life satisfaction.
Copyright: © 2025 Ye et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Costanza R, Fisher B, Ali S, Beer C, Bond L, Boumans R, et al. Quality of life: An approach integrating opportunities, human needs, and subjective well-being. Ecological Economics. 2007;61(2–3):267–76. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2006.02.023 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous