Research hotspots and emerging topics in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder treatment: Insights from a bibliometric analysis
- PMID: 40489809
- PMCID: PMC12150997
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042850
Research hotspots and emerging topics in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder treatment: Insights from a bibliometric analysis
Abstract
Object: Effective treatment of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) can greatly reduce the rate of disability and mortality among patients. NMOSD treatment studies are gaining prominence in academic circles. This study aims to depict the evolution and integration of NMOSD treatment over the past 20 years, identify key contributors in the field, clarify current research hotspots, and explore emerging topics that may guide future research directions.
Method: Articles in this field from 2004 to 2023 were collected from the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC). After conducting a literature search, a comprehensive bibliometric and knowledge mapping analysis was carried out on the retrieved articles using tools such as VOSviewer, Bibliometrix, and CiteSpace.
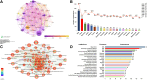
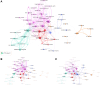
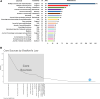
Result: The rapid growth in annual publications in this field indicates rapid progress and innovation. USA, Mayo Clinic, and Fujihara K led in productivity and impact, while the multiple sclerosis and related disorders topped in publication volume. The research hotspots in this field mainly focus on targeted biological agents. Additionally, this study has identified 3 emerging themes and conducted an in-depth exploration of their future development trends.
Conclusion: In summary, this bibliometric analysis provides for the first time a comprehensive framework and frontier hot spot analysis in the field of NMOSD treatment, offering references for researchers in the field and contributing to the further development of the field.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04227470.
Keywords: NMOSD; bibliometrics; developing trends; neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder; treatment; visual analysis.
Copyright © 2025 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Uzawa A, Oertel FC, Mori M, Paul F, Kuwabara S. NMOSD and MOGAD: an evolving disease spectrum. Nat Rev Neurol. 2024;20:602–19. - PubMed
-
- P P, Mp A, L B, et al. Moving towards a new era for the treatment of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. J Neurol. 2024;271:3879–96. - PubMed
-
- Yong HYF, Burton JM. A clinical approach to existing and emerging therapeutics in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2023;23:489–506. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

