Causal validation between 179 lipids and hyperparathyroidism: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization combined meta-analysis with mediation factors
- PMID: 40489840
- PMCID: PMC12150918
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042580
Causal validation between 179 lipids and hyperparathyroidism: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization combined meta-analysis with mediation factors
Abstract
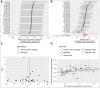
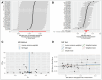
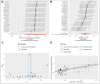
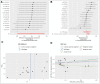
Hyperparathyroidism, an endocrine disorder linked to hypercalcemia, increases with age, particularly in those over 60. Abnormal lipid metabolism may be closely related to its occurrence and progression. The study used Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis on 179 lipid traits against hyperparathyroidism in the Finngen and UK Biobank (UKB) databases. Meta-analysis of inverse variance weighted results followed, with significance P-values corrected for multiple comparisons. Causal validation was performed between positive lipids and renal failure, and MR analysis examined the link between renal failure and hyperparathyroidism. Reverse causal validation was also conducted between lipids and hyperparathyroidism, positive lipids and renal failure, and renal failure and hyperparathyroidism. The study conducted causal validation between 179 lipid traits and hyperparathyroidism, also exploring intermediary factors. Ultimately, MR analysis was performed on triacylglycerol (52:3) levels with hyperparathyroidism in both Finngen and UKB databases, followed by meta-analysis and multiple corrections. The results showed an odds ratio (OR) of 1.147 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.065-1.235, P = .040). The MR results for triacylglycerol (52:3) levels and renal failure indicated an OR of 1.054 (95% CI: 1.004-1.106, P = .032). For the intermediary factor renal failure, MR analysis with hyperparathyroidism in both Finngen and UKB databases followed by meta-analysis showed an OR of 1.336 (95% CI: 1.193-1.495, P = 4.78 × 10-7). Notably, no significant associations were found in the reverse validation of each analysis process. Furthermore, the mediation effect was β12 = 0.0153, and the direct effect was β3 = 0.1207 (0.1183, 0.1230). The mediation effect accounted for 11.25%, while the direct effect accounted for 88.75% of the total effect, Z = 12.5, indicating that the direct effect predominantly influences the overall impact. The research shows that triacylglycerol (52:3) levels can directly increase the risk of hyperparathyroidism. It also raises the risk indirectly by increasing the likelihood of renal failure, an intermediary factor. About one-tenth of the lipid's effect on hyperparathyroidism is mediated through renal failure, while the direct effect constitutes roughly nine-tenths of the total effect.
Keywords: Mendelian randomization analysis; hyperparathyroidism; lipids; meta-analysis; multiple corrections; renal failure; reverse Mendelian randomization analysis.
Copyright © 2025 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

