Temporal single-cell sequencing analysis reveals that GPNMB-expressing macrophages potentiate muscle regeneration
- PMID: 40490493
- PMCID: PMC12229484
- DOI: 10.1038/s12276-025-01467-4
Temporal single-cell sequencing analysis reveals that GPNMB-expressing macrophages potentiate muscle regeneration
Abstract
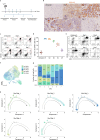
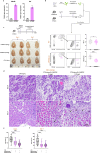
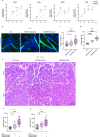
Macrophages play a crucial role in coordinating the skeletal muscle repair response, but their phenotypic diversity and the transition of specialized subsets to resolution-phase macrophages remain poorly understood. Here, to address this issue, we induced injury and performed single-cell RNA sequencing on individual cells in skeletal muscle at different time points. Our analysis revealed a distinct macrophage subset that expressed high levels of Gpnmb and that coexpressed critical factors involved in macrophage-mediated muscle regeneration, including Igf1, Mertk and Nr1h3. Gpnmb gene knockout inhibited macrophage-mediated efferocytosis and impaired skeletal muscle regeneration. Functional studies demonstrated that GPNMB acts directly on muscle cells in vitro and improves muscle regeneration in vivo. These findings provide a comprehensive transcriptomic atlas of macrophages during muscle injury, highlighting the key role of the GPNMB macrophage subset in regenerative processes. Our findings suggest that modulating GPNMB signaling in macrophages may represent a promising avenue for future research into therapeutic strategies for enhancing skeletal muscle regeneration.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Update of
-
Temporal Single-Cell Sequencing Analysis Reveals That GPNMB-Expressing Macrophages Potentiate Muscle Regeneration.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Mar 28:rs.3.rs-4108866. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4108866/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Exp Mol Med. 2025 Jun;57(6):1232-1245. doi: 10.1038/s12276-025-01467-4. PMID: 38585871 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Giordani, L. et al. High-dimensional single-cell cartography reveals novel skeletal muscle-resident cell populations. Mol. Cell74, 609–621 (2019). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

