Oral manifestations in patients with chronic hepatitis C
- PMID: 40490688
- PMCID: PMC12150542
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-025-06307-5
Oral manifestations in patients with chronic hepatitis C
Abstract
Background: Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, a systemic disease characterized by extrahepatic manifestations (EMs), affects approximately 50 million people worldwide. Recognizing EMs, which may involve multiple organs and systems, is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective antiviral therapy. Purpose of the study was to investigate extrahepatic symptoms occurring in the oral mucosa in HCV-infected patients.
Methods: The observational study included 153 consecutive patients with chronic hepatitis C and healthy controls. Data collection encompassed demographic parameters, medical history, laboratory results, and oral examinations, which included evaluation of dry mouth, pain and burning in the mouth and on the tongue, pain in the angles of the mouth, bad breath, gingival bleeding, dysphagia and taste disorders using scales designed for this purpose, clinical and dental examination.
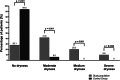
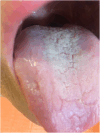
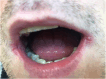
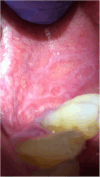
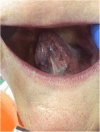
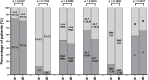
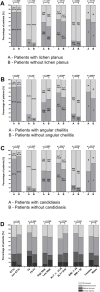
Results: Subjective oral symptoms were twice as common in the study group as in controls with the most frequent dry mouth, followed by oral pain, and burning in the mouth. Pathological changes (oral candidiasis, angular cheilitis and lichen planus), were identified in 73.2% of patients, compared to 32% in the control group. Oral hygiene was worse in the study group with a median score of 1.8 compared to 1.1 as assessed by the Oral Hygiene Index scale. The incidence of Mikulicz's aphthae, papillomas, fibromas and sublingual varices did not reach statistically significant differences. The study group had fewer teeth with dental fillings. Additionally, age ≥ 40 years and GT1 infection were identified as independent predictors of oral pathologies in HCV-infected patients.
Conclusions: In patients with chronic HCV infection, oral mucosal pathologies were significantly more common compared to controls, with candidiasis, angular cheilitis, and oral lichen planus being the most frequently observed conditions. Subjective symptoms such as dry mouth, oral pain, and burning were also markedly higher in the HCV group. Age ≥ 40 years and GT1b HCV genotype were identified as independent positive predictors of oral mucosal lesions.
Keywords: Chronic hepatitis C; Extrahepatic manifestations; Hepatitis C virus; Oral lichen planus; Oral pathologies.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was conducted after the approval of the Bioethics Committee of the Jan Kochanowski University in Kielce by resolution No. 18/2018 of 26.03.2018 and access to medical records and use of data on the treatment of patients was made with the prior consent of the Hospital Management. All patients were included in the study after being fully informed about the purpose of the study and providing their written consent to participate, demonstrating their awareness and understanding. The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oral mucosa alterations in chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis due to HBV or HCV infection.Bull Group Int Rech Sci Stomatol Odontol. 2006 Mar;47(1):6-10. Bull Group Int Rech Sci Stomatol Odontol. 2006. PMID: 17672199
-
Oral findings in chronic kidney disease: implications for management in developing countries.BMC Oral Health. 2015 Feb 20;15:24. doi: 10.1186/s12903-015-0004-z. BMC Oral Health. 2015. PMID: 25888327 Free PMC article.
-
Oral health of patients with hepatitis C virus infection: a pilot study.Oral Dis. 2001 Sep;7(5):271-5. doi: 10.1034/j.1601-0825.2001.00695.x. Oral Dis. 2001. PMID: 12117200
-
A personal journey through Oral medicine: The tale of hepatitis C virus and oral lichen planus.J Oral Pathol Med. 2023 Apr;52(4):335-338. doi: 10.1111/jop.13400. Epub 2023 Jan 12. J Oral Pathol Med. 2023. PMID: 36597838 Review.
-
Oral diseases associated with hepatitis C virus infection. Part 2: lichen planus and other diseases.Oral Dis. 2008 Apr;14(3):217-28. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-0825.2007.01432.x. Epub 2008 Jan 22. Oral Dis. 2008. PMID: 18221456 Review.
References
-
- Martinello M, Solomon SS, Terrault NA, Dore GJ. Hepatitis C. Lancet. 2023;402:1085–96. 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)01320-X. - PubMed
-
- Hepatitis C. [cited 27 Apr 2025]. Available: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-c
-
- Cacoub P, Saadoun D. Extrahepatic manifestations of chronic HCV infection. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:1038–52. 10.1056/NEJMra2033539. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

